![]()
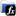 Function
Function![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs.
A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Extract the value of a variable from a binary frame
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs.
A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Extract the value of a variable from a binary frame![]() In networking dialect, a message is called a frame..
In networking dialect, a message is called a frame..
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
En |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
Execute the function. |
|
Frame[ ] |
USINT |
0,+65535 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
Data |
ANY(*) |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
Destination variable to be copied. |
|
Pos |
DINT |
0,+65535 |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
BigEndian |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
TRUE if the frame is encoded |
(*) DATA cannot be a STRING.
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
OK |
BOOL |
|
N/A |
Returns TRUE when the function successfully executes. |
|
NextPos |
DINT |
|
N/A |
|
Remarks
- Used to extract data from a communication frame in binary format.
- This function cannot be used to serialize STRING variables.
- The DATA input must be directly
 The orientation components of a vector in space. connected to a variable.
The orientation components of a vector in space. connected to a variable. - It cannot be a constant or complex expression.
- This variable is forced with the extracted value.
- The FRAME input must fit the input position and data size.
- If the value cannot be safely extracted, the function returns 0 (zero).
- The function returns the position in the source frame after the extracted data.
- The return value can be used as a position for the next serialization.
This function extracts these number of bytes from the source frame:
| Bytes | Description |
|---|---|
|
1 byte |
BOOL, BYTE, SINT, and USINT variables. |
|
2 bytes |
INT, UINT, and WORD variables. |
|
4 bytes |
DINT, DWORD, REAL, and UDINT variables. |
|
8 bytes |
LINT and LREAL variables. |
FBD Language Example
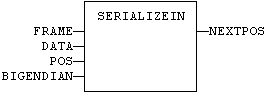
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD Language, the operation is executed only if the input rung (EN) is TRUE.
- The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung.
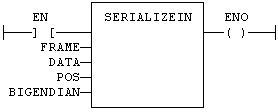
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
Q := SERIALIZEIN (FRAME, DATA, POS, BIGENDIAN);
See Also






