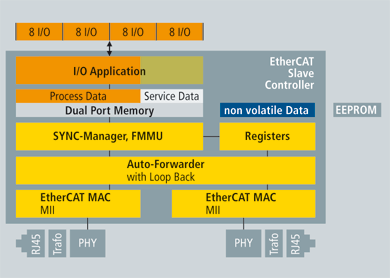
Slave Configuration
A cost-effective EtherCAT![]() EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs slave controller (ESC) is used in the slave devices. With EtherCAT the slave does not need a microcontroller at all. Simple devices that get by with an I/O interface can be implemented only with the ESC and the RJ45 connector. The process data interface (PDI) to the slave application is a 32-bit I/O interface. This slave without configurable parameters needs no software or mailbox protocol. The EtherCAT State Machine is handled in the ESC. The boot-up information for the ESC comes out of the EEPROM that also supports the identity information of the slave. More complex slaves that are configurable have a host CPU on board. This CPU is connected to the ESC with an 8-bit or 16-bit parallel interface or via a serial connection.
EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs slave controller (ESC) is used in the slave devices. With EtherCAT the slave does not need a microcontroller at all. Simple devices that get by with an I/O interface can be implemented only with the ESC and the RJ45 connector. The process data interface (PDI) to the slave application is a 32-bit I/O interface. This slave without configurable parameters needs no software or mailbox protocol. The EtherCAT State Machine is handled in the ESC. The boot-up information for the ESC comes out of the EEPROM that also supports the identity information of the slave. More complex slaves that are configurable have a host CPU on board. This CPU is connected to the ESC with an 8-bit or 16-bit parallel interface or via a serial connection.
EtherCAT Slave Controller
The slave controllers typically feature an internal DPRAM and offer a range of interfaces for accessing this application memory:
- The SPI (serial peripheral interface bus) is intended particularly for devices with small process data quantity, such as analog I/O modules, sensors, encoders or simple drives.
- The parallel 8/16-bit microcontroller interface corresponds to conventional interfaces for fieldbus controllers with DPRAM interface. It is particularly suitable for more complex devices with larger data volume.
- The 32-bit parallel I/O interface is suitable for the connection of up to 32 digital inputs/outputs, but also for simple sensors or actuators
 A mechanical device for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. An actuator typically is a mechanical device which transforms an input signal (usually an electrical signal) into motion operating with 32 data bits. Such devices do not need a host CPU at all (as shown in Slave Hardware: FPGA with direct I/O).
A mechanical device for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. An actuator typically is a mechanical device which transforms an input signal (usually an electrical signal) into motion operating with 32 data bits. Such devices do not need a host CPU at all (as shown in Slave Hardware: FPGA with direct I/O).
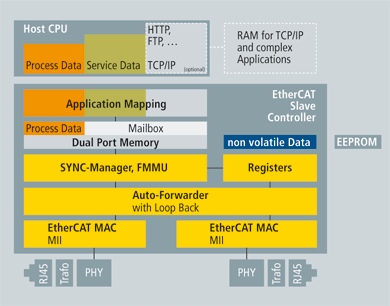
Figure 5-61: Slave Hardware: FPGA with Host CPU