Acronyms
| Term | Definition | Description |
|
AKA |
Also Known As |
Provides an alias to a name |
|
AKD |
Advanced Kollmorgen Drive |
|
|
AKI |
Advanced Kollmorgen Interface |
|
|
AKT |
Advanced Kollmorgen Terminal |
|
|
ANSI |
American National Standards Institute |
ANSI is a private, nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel |
|
ASFB |
Application Specific Function Block |
Library that can be written to provide a specific application task |
|
ASIC |
Application-Specific Integrated Circuit |
An ASIC is an integrated circuit (IC |
|
BiSS |
Bi-directional Serial Synchronous interface |
An open-source communication protocol for feedback devices. With BiSS, all of the computation for interpolation in regard to position occurs on the ASIC |
|
CAM |
Computer-Aided Manufacturing |
CAM means the use of a wide range of computer-based software tools that assist engineers and CNC machinists in the manufacture or prototyping of product components |
|
CAN |
Controller Area Network |
CAN is a broadcast, differential serial bus standard developed for connecting electronic control units. Each node is able to send and receive messages, but not simultaneously.
|
|
CF |
Compact Flash |
CF is a mass storage device format used in portable electronic devices |
|
CIP |
Common Industrial Protocol |
The Common Industrial Protocol allows complete integration of control with information, multiple CIP Networks, and Internet technologies |
|
CRC |
Cyclic Redundancy Check |
A CRC is a type of function that takes as input a data stream of any length and produces as output a value of a certain fixed size. The term CRC is often used to denote either the function or the function's output. A CRC can be used as a checksum to detect accidental alteration of data during transmission or storage |
|
CSV |
Comma-Separated Values |
CSV file format is a file type that stores tabular data |
|
DMA |
Dynamic Memory Allocation |
DMA is the allocation of memory storage for use in a computer program during the run-time |
| EDS | Electronic Data Sheet | The Electronic Data Sheet is a file format that defines the communication behavior and object dictionary for the devices following the CANopen standard CiA 306. EtherCAT |
| ENI | EtherCAT Network Information |
A network configuration file in XML The KAS IDE |
|
ERP |
Enterprise Resource Planning |
ERP integrates (or attempts to integrate) all data and processes of an organization into a unified system |
| ESI | EtherCAT Slave Information |
A device description in XML format. This is a fixed file provided by the supplier of a given EtherCAT device. The ESI file contains information about the device's functionality and settings. EtherCAT device vendors must provide an ESI file, which is used by the KAS IDE to compile the network information (e.g. process data structures, initialization commands) and create the ENI file. |
|
FBD |
A function block diagram describes a function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks |
|
|
Free Form Ladder Diagram |
Free Form Ladder logic is a method of drawing electrical logic schematics. It is now a very popular graphical language for programming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). It was originally invented to describe logic made from relays. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical "rails" and a series of horizontal "rungs" between them |
|
|
FoE |
File over EtherCAT |
This very simple protocol, similar to TFTP, enables access to any data structure in the device. Standardized firmware upload to devices is therefore possible, irrespective of whether or not they support TCP/IP |
|
FPGA |
Field-Programmable Gate Array |
FPGA is a semiconductor device that can be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing; hence the name "field-programmable" |
|
FailSafe over EtherCAT |
The protocol FSoE was specified for the transmission of safety relevant data. It is used to send input information of safety sensors (such as safety light curtains or emergency stop buttons) to a safety logic controller. Based on these inputs, this controller computes the commands for the safe outputs (such as contactors or safety relevant drives) and thus controls the safety functionality of the machine |
|
|
GUI |
Graphical User Interface |
A GUI is a type of user interface which allows people to interact with a computer and computer-controlled devices |
|
HMI |
Human-Machine Interfaces |
Also known as computer-human interfaces (CHI), and formerly known as man-machine interfaces, they are usually employed to communicate with PLCs and other computers, such as entering and monitoring temperatures or pressures for further automated control or emergency response |
|
IC |
Integrated Circuits |
Miniaturized electronic circuits (consisting mainly of semiconductor devices, as well as passive components) that have been manufactured in the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material |
|
IDE |
Integrated Development Environment |
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software. |
|
IDN |
Identification Number |
An IDN preceded by the prefix "P", specifies a product specific (manufacturer) IDN in short-hand notation. The actual IDN number for a product-specific IDN, can be obtained by adding 32768 to the short-hand numeric value. For convenience, the actual IDN number is given in parentheses following the short hand notation. For example, P2 is a manufacturer-specific IDN whose actual IDN number is 32770 |
|
IEC |
International Electrotechnical Commission |
IEC is a not-for-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies |
|
IEC 61131 |
|
IEC |
|
IEC 61131-3 |
|
IEC 61131-3 is the third part of the open international standard IEC 61131. The current (second) edition was published in 2003. |
|
IL |
Instruction List |
It is a low-level language and resembles assembly |
|
IPC |
Industrial PC |
Industrial PC is the x86 PC-based computing platform for industrial applications. Industrial PC offers features different from the consumer PC on the reliability, compatibility, expansibility and long term supply. |
|
IRQ |
An interrupt request refers to the act of interrupting the bus lines used to signal an interrupt |
|
|
JTAG |
Joint Test Action Group |
JTAG is used for accessing sub-blocks of integrated circuits, and is also useful as a mechanism for debugging embedded systems, providing a convenient "back door" into the system. When used as a debugging tool, an in-circuit emulator - which in turn uses JTAG as the transport mechanism - enables a programmer to access an on-chip debug module which is integrated into the CPU via the JTAG |
|
KAS |
Kollmorgen Automation Suite |
Umbrella name for a software package including the KAS IDE and the KAS Runtime |
|
KAS IDE |
Kollmorgen Automation Suite - Integrated Development Environment |
The KAS IDE is the GUI |
|
KAS Runtime |
Kollmorgen Automation Suite - Runtime |
The KAS Runtime is the engine that provides a soft PLC and a motion controller |
|
KVB IDE |
Kollmorgen HMI |
Kollmorgen Visualization Builder is an editor that allows the end-user to control the KAS Runtime |
|
LD |
Ladder Diagram |
|
|
LSB |
Least Significant Bit |
Sometimes abbreviated as LSB, the least significant bit is the lowest bit in a series of numbers in binary; the LSB is located at the far right of a string. For example, in the binary number: 10111001, the least significant bit is the far right "1". |
|
MDI |
Multiple Document Interface |
Graphical computer applications with an MDI are those whose windows reside under a single parent window (usually with the exception of modal windows), as opposed to all windows being separate from each other (single document interface). Advantages: - With MDI, a single menu bar and/or toolbar is shared between all child windows, reducing clutter and increasing efficient use of screen space - An application's child windows can be hidden/shown/minimized/maximized as a whole - Features such as "Tile" and "Cascade" can be implemented for the child windows |
|
ML |
Motion Library |
The Motion Library is the interface between the IEC61131-3 |
|
MSB |
Most Significant Bit |
Sometimes abbreviated as MSB, the most significant bit is the bit position in a binary number having the greatest value |
| MDP | Modular Device Profile | The EtherCAT Modular Device Profile defines the data structure organization for a device with subdivided substructures. The object dictionary structure, the PDO structure, and their corresponding indexes are defined by the MDP specification. This makes it possible for the EtherCAT master to support a variety of modular device types from different manufacturers. MDP supports devices with either physical plug-in modules or logical modules, enabling users to assemble scalable devices or select from a range of pre-built devices with various feature sets. |
|
NAT |
Network Address Translation |
In computer networking, NAT is the process of modifying network address information in datagram (IP) packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device for the purpose of remapping a given address space into another. |
|
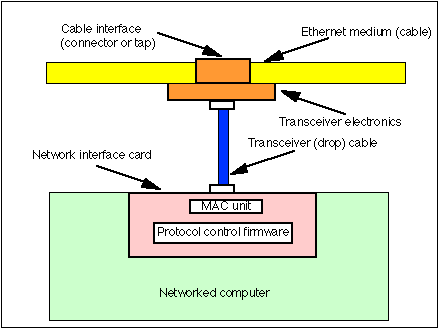
NIC |
Network Interface Controller |
A network interface controller (or card) is a hardware device that handles an interface to a computer network and allows a network-capable device to access that network
|
|
NVRAM |
Non-Volatile Random Access Memory |
NVRAM is the general name used to describe any type of random access memory which does not lose its information when power is turned off. This memory is in contrast to the most common forms of random access memory today, which both require continual power in order to maintain their data. NVRAM is a subgroup of the more general class of non-volatile memory types, the difference being that NVRAM devices offer random access, like hard disks. The best-known form of NVRAM memory today is flash memory |
|
OEM |
Original Equipment Manufacturer |
A term that refers to containment-based re-branding, namely where one company uses a component of another company within its product, or sells the product of another company under its own brand. OEM refers to the company that originally manufactured the product |
|
OPC |
OLE for Process Control |
OPC is the original name for an open standard to specify the communication of real-time plant data between control devices from different manufacturers |
|
PCI |
Peripheral Component Interconnect |
The PCI specifies a computer bus for attaching peripheral devices to a computer motherboard |
|
PCMM |
Programmable controller which lets you control multiple EtherCAT slave drives and I/O. Essentially a AKD PDMM without an AKD. |
|
|
PD |
Programmable Drive |
(Also known as Servo Amplifiers or Servo Drive |
|
PDMM |
Programmable Drive Multi-axis Master |
Programmable drive which lets you control multiple EtherCAT slave drives and I/O |
|
Process Data Object |
PDO is a type of protocol frame used in some fieldbuses EtherCAT uses the same communication mechanisms (PDO and SDO) as CANopen. EtherCAT transfers the process data between the master and slave device cyclically. PDOs have several attributes to define their properties.
|
|
|
PID |
Proportional-Integral-Derivative |
A PID controller is a generic control-loop feedback mechanism widely used in industrial control systems. An "error" occurs when an event or a disturbance triggers off a change in the process variable. A PID controller attempts to correct the error between a measured process variable and a desired setpoint |
|
PLC |
Programmable Logic Controller |
A Programmable Logic Controller, PLC, or Programmable Controller is a digital computer used for automation of industrial processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines. |
|
PNE |
Pipe Network Engine |
The Pipe Network concept is an innovative solution to solve axis synchronization problems. |
|
POU |
Programmable Organization Unit |
An application is a list of programs. Programs are executed sequentially within the target cycle according to the order defined by the user and displayed in the Project View |
|
Qwt |
Qt Widgets |
Qwt is a graphics extension to the Qt GUI application framework from Trolltech ASA |
|
RTC |
Real-Time Computing |
RTC is the study of hardware and software systems which are subject to a "real-time constraint" (i.e., operational deadlines from event to system response) |
|
RTOS |
Real-Time Operating System |
RTOS is a multitasking operating system intended for real-time applications |
|
S300 |
Servostar 300 drive |
|
|
S700 |
Servostar 700 drive |
|
|
SCADA |
Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition |
SCADA systems are typically used to perform data collection and control at the supervisory level. Some SCADA systems only monitor without doing control, these systems are still referred to as SCADA systems |
|
Service Data Object |
The SDO protocol is used to read and write values across fieldbuses . The SDO data is defined by the object dictionary. EtherCAT uses the same communication mechanisms (PDO and SDO) as CANopen. SDO data is non-cyclic and is applicable for non-deterministic data transfers. |
|
|
SFC |
Sequential Function Chart |
It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps. |
|
SPLC |
Software version of a PLC |
Usually working on PC-based hardware |
|
ST |
Structured Text |
A high-level language which is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal |
|
TDI |
Tabbed Document Interface |
TDI allows multiple documents to be contained within a single window, using tabs to navigate between them |
|
TMP |
Trapezoidal Motion Profile |
This Pipe Block is a source block that frequently serves as a virtual master for a system composed of several pipes. Generally, a trapezoidal motion profile generator is used to generate a flow of values with a first derivative which produces a trapezoidal trajectory |
|
UDFB |
User-Defined Function Block |
UDFB can be used as a sub-Function Block in another program of the application. It is described using FBD |
|
User Datagram Protocol |
UDP is a network protocol used for the Internet. This protocol assumes that the Internet Protocol (IP) is used as the underlying protocol. This protocol provides a procedure for application programs to send messages to other programs with a minimum of protocol mechanism. The protocol is transaction oriented, and delivery and duplicate protection are not guaranteed. |
|
|
USB |
Universal Serial Bus |
USB is a serial bus standard to interface devices |
|
UTF8 |
Unicode Transformation Format (8-bit) |
UTF-8 is a variable-length character encoding for Unicode. It is able to represent any character in the Unicode standard, yet the initial encoding of byte codes and character assignments for UTF-8 is backward-compatible with ASCII |
|
UU |
User Units |
A coordinate value or length expressed in user units represents a coordinate value or length in the current user coordinate system. Thus, 10 user units represent a length of 10 units in the current user coordinate system. |
|
XML |
Extensible Markup Language |
XML is a general-purpose markup language. It is classified as an extensible language because it allows its users to define their own tags |
|
VDK |
VisualDSP Kernel |
Operating system supported by Blackfin microprocessors |
|
VLAN |
Virtual LAN |
A VLAN is a group of hosts with a common set of requirements that communicate as if they were attached to the Broadcast domain, regardless of their physical location. A VLAN has the same attributes as a physical LAN, but it allows for end stations to be grouped together even if they are not located on the same network switch. Network reconfiguration can be performed using software instead of physically relocating devices |
|
XPe |
Windows XP Embedded |
XPe is a componentized version of the Professional edition of Windows XP. An original equipment manufacturer is free to choose only the components needed, thereby reducing operating system footprint and also reducing attack area as compared with XP Professional. Unlike Windows CE, Microsoft's operating system for portable devices and consumer electronics, XP Embedded provides the full Windows API, and support for the full range of applications and device drivers written for Microsoft Windows. The system requirements state that XPe can run on devices with at least 32MB Compact Flash, 32MB RAM and a P-200 microprocessor |
|
WUI |
Web User Interface |
WUI is the set of means by which people interact with a particular machine, device, computer program or other complex tool via the Web |