Coordinate Systems
There are three different coordinate system (CS) types:
- Machine (MCS)
- Axes (ACS)
- Product/Program (PCS)
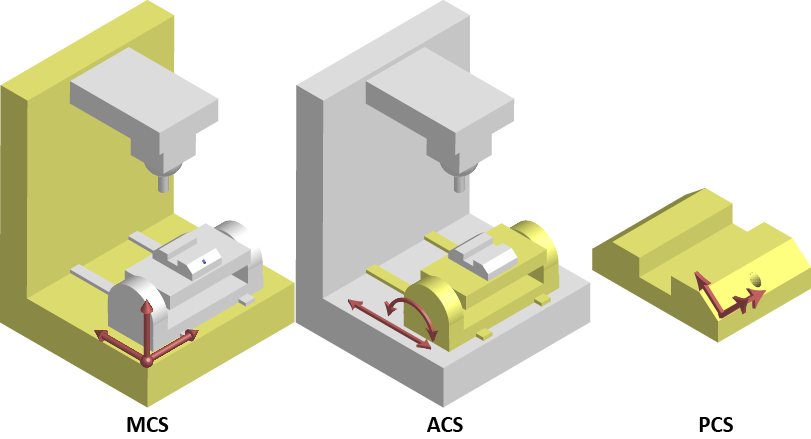
Figure 8-1: Examples of CS types on a machine and part.
Many coordinated moves may be done in a choice of coordinate systems. The differences between the types are offsets and possibly transformational algorithms to convert between the different systems, which ultimately control the actual axes on a piece of machinery.
For example, the X-axis of a Machine CS is meant to command a pair of Axes CS axes (X1 and X2) which together form a gantry. The relative movement of the MCS X axis would be added to both ACS axes. The two ACS axes can also be commanded independently for minor alignment adjustments.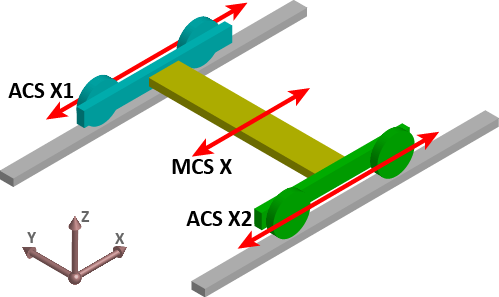
-
-
The Product Coordinate System is often rotated and/or offset from the Machine Coordinate System.






