Glossary
Terms in this Glossary are provided for informational purposes only and can describe features not included in your particular license.
| Term | Definition |
| Actuator | A mechanical device for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. An actuator typically is a mechanical device which transforms an input signal (usually an electrical signal) into motion |
| Bandwidth | In computer networking, bandwidth often refers to a data rate measured in bits/s, for example, network throughput. The reason for the connection of data rate with the term bandwidth is that the limit to the data rate of a physical communication link is related to its bandwidth in hertz |
| Black Channel |
A Black Channel allows transmission of safety data via the standard network line. Safety over EtherCAT |
| Cam profiling | The position of a slave axis is mathematically linked to the position of a master axis. A good example of this would be in a system where two rotating drums turn at a given ratio to each other. A more advanced case of electronic gearing is electronic camming. With electronic camming, a slave axis follows a profile which is a function of the master position. This profile need not be linear, but it must be a mathematical function |
| CANopen |
CANopen is a communication protocol and device profile specification for embedded systems used in automation for fieldbuses
|
| Caret | The term caret is also sometimes used in graphical user interface terminology where it means a text insertion point indicator, frequently represented by a blinking vertical bar. In this context, it can be used interchangeably with the word cursor, although the latter term is often reserved for a mouse pointer |
| Casting | For Typecasting, Typecasting |
| Closed Loop |
The use of feedback devices (encoders, resolvers, interferometers, etc.) to allow a motor to position a user payload accurately. |
| COM | COM is the original name of the serial port interface. It does not only refer to physical ports, but also to virtual ports, such as ports created by bluetooth or USB |
| Contactor | A contactor is an electrically controlled switch (relay) used for switching a power circuit. A contactor is activated by a control input which is a lower voltage/current than that which the contactor is switching. Unlike a circuit breaker, a contactor is not intended to interrupt a short-circuit current |
| Cycle Jitter |
The difference between the configured cycle time and the actual meausured cycle time. Units in microseconds. |
| Datagram | A datagram is a basic transfer unit in which the delivery arrival time and order are not guaranteed. A datagram consists of header and data areas. The source and destination addresses as well as a type field are found in the header of a datagram. |
| DeviceNet | DeviceNet is a communication protocol (based on Controller Area Network) used in the automation industry to interconnect control devices for data exchange. Typical applications are information exchange, safety devices, and large I/O control networks |
| Drive | In electrical engineering, a drive is an electronic device providing power to a servo or stepper motor, and controlling it through the current and timing in its coils |
| Driver | In computing and electronics, a driver is a software component allowing higher-level computer programs to interact with a computer hardware device. A driver typically communicates with the device through the computer bus or communications subsystem to which the hardware is connected |
| Endian, endianness |
Big-endian and little-endian describe the order in which a sequence of bytes are stored in computer memory. Big-endian is an order in which the "big end" (most significant value in the sequence) is stored first (at the lowest storage address). Little-endian is an order in which the "little end" (least significant value in the sequence) is stored first For example the decimal integer 56789652 (0x03628a94 in hexadecimal) is stored as follows:
KAS applications can be downloaded to big-endian or little-endian processor targets |
| Environment | Environment objects are global objects that exist before the execution of the script. Typically, they are global objects of the KAS IDE |
| EtherCAT |
"Ethernet EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs
|
| Ethernet | Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs) |
| EtherNet/IP | An open industrial application layer protocol for industrial automation applications. The EtherNet/IP application layer protocol is based on the CIP |
| Fast Inputs | The inputs are taken into account at each cycle depending on the system periodicity (for example each millisecond). Under certain circumstances it can be insufficient when more accuracy is needed, or if a quick response is required from the system. To fill the gap, a drive can have some Fast Input connections (generally one or two). When an event happens that triggers a Fast Input (e.g. when a sensor |
| Feedback Device | A process whereby some proportion of the output signal of a system is passed (fed back) to the input. In automation, a device coupled to each motor to provide indication of the motor's shaft angle, for use in commutating the motor and controlling its speed and position |
| feed-forward | This describes an element or pathway within a control system which passes a controlling signal from a source in the control system's external environment, often a command signal from an external operator, to a load elsewhere in its external environment |
| Fieldbus | A Fieldbus is an industrial network protocol used for distributed control (e.g. EtherCAT, CAN |
| Flash Memory | A Flash memory is a non-volatile computer storage chip that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. In addition to being non-volatile, flash memory offers fast read access times, as fast as dynamic RAM, although not as fast as static RAM or ROM. Its mechanic shock resistance explain the popularity over hard disks in portable devices; so does its high durability, being able to withstand high pressure, temperature, immersion in water etc. |
| Frame |
In networking dialect, a message is called a frame |
| Front-end | In software design, the front-end is the part of a software system that interacts directly with the user |
| Homing | The Homing procedure allows, based on a position measurement, to set a position offset to the motor in order to ensure it is physically at the home position. The homing offset is saved in the controller. |
| Interrupt | An interrupt is an asynchronous signal from hardware indicating the need for attention or a synchronous event in software indicating the need for a change in execution |
| Jerk | In physics, jerk is the rate of change of acceleration; more precisely, the derivative of acceleration with respect to time |
| Latch | The control word is used to activate the drive's latch status machine. The latch control word is processed independently of the EtherCAT bus cycle. The status word is used to return the drive's latch status |
| MAC address | A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a quasi-unique identifier assigned to most network adapters or network interface cards (NICs) by the manufacturer for identification. If assigned by the manufacturer, a MAC address usually encodes the manufacturer's registered identification number |
| ModBus |
ModBus is a serial communications protocol and is now the most commonly available means of connecting industrial electronic devices. ModBus is often used to connect a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit in supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Versions of the ModBus protocol exist for serial port and Ethernet (it is widely used with TCP/IP over Ethernet) |
| Motion Bus | A Motion bus is an industrial network protocol used for real-time distributed control (e.g. EtherCAT). |
| Motion control | Motion control is a sub-field of automation, in which the position and/or velocity of machines are controlled using some type of device such as a hydraulic pump, linear actuator |
| Motor | An actuator focused to a movement, converting electrical energy in a force or torque |
| Non-volatile | Information is stored in a specific memory to remain accessible even when the application has been powered off |
| Online Change | Applies to downloading PLC |
| Online Configuration Mode | Applies to EtherCAT communication to the AKD drives in a special mode. |
| Open Loop |
A positioning technique, typically utilizing stepper motors, in which the controller issues a sequence of commands to the motor without any absolute means of detecting if the move has in fact been made. When the load and move velocity and acceleration are appropriately defined, open loop |
| OpenGL | OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a standard specification defining a cross-language, cross-platform API for writing applications that produce 2D and 3D computer graphics. The Softscope uses this API to implement graphical manipulations |
| P-code | P-code machine or pseudo-code machine is a specification of a CPU whose instructions are expected to be executed in software rather than in hardware. Programs that have been translated to P-code are executed (interpreted) by a software program that emulates the behavior of the CPU specification |
| PDO |
PDO is a type of protocol frame used in some fieldbuses. A PDO contains one or more object dictionary entries, which define the application data transferred between devices. EtherCAT uses the same communication mechanisms (PDO and SDO) as CANopen. EtherCAT transfers the process data between the master and slave device cyclically. PDOs have several attributes to define their properties.
|
| Periodicity | The period of execution of a pipe is the time spent between two successive computations of set values for the same pipe. The period of execution of a pipe is specified by the PERIOD parameter of the input Pipe Block |
| PLCopen | A vendor -and product- independent worldwide association active in Industrial Control and aiming at standardizing PLC file formats based on XML |
| Pragma |
A compiler directive communicating additional "pragmatic" information. Pragmas are processed at compile time, not at run-time |
| Precedence | In arithmetic and algebra, when a number or expression is both preceded and followed by a binary operation, a rule is required for which operation must be applied first. From the earliest use of mathematical notation, multiplication took precedence over addition, whichever side of a number it appeared on. Thus 3 + 4 × 5 = 5 × 4 + 3 = 23. To change the order of operations, we use parentheses (). Thus, if we want to force addition to precede multiplication, we write (3 + 4) × 5 = 35 |
| Probe | For Softscope -Probe, Softscope - Probe |
| Pulse | When the step gets activated, the action is activated for a single execution, and possibly once again when the step is deactivated |
| Reference Counting | In computer science, reference counting is a technique of storing the number of references, pointers, or handles to a resource such as an object or block of memory. It is typically used as a means of deallocating objects which are no longer referenced |
| Rising Edge | A rising edge is the transition of a digital signal from low to high. It is also called positive edge |
| Run-time | In computer science, run-time (or run time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time) |
| Sensor | A sensor is a type of transducer that converts one type of energy into another for various purposes including measurement or information transfer |
| Service Port | UDP applications use datagram sockets to establish host-to-host communications. An application binds a socket to its endpoint of data transmission, which is a combination of an IP address and a service port. A port is a software structure that is identified by the port number, a 16 bit integer value. |
| Servo Drive | A servo drive is a special electric amplifier used to power electric servo motors. It monitors feedback signals from the motor and continually adjusts for deviation from expected behavior |
| Setpoint | Setpoint is the target value that an automatic control system (for example a PID |
| Softscope - Channel | A Channel is used by the softscope to acquire the evolution of a variable which is plugged on it |
| Softscope - Probe | A device that uses onboard instruments to gather and relay a variety of measurement to controllers from remote locations. Probes can return their data over radio links or be physically tethered to controllers or another device, or to collect and return physical samples |
| Softscope - Sampling | To acquire the variable's evolution, samples are taken at fixed intervals. The accuracy to create the trace depends on the resolution of the acquisition. The sampling frequency must be higher than 2 times the highest frequency in the input signal. It is called the Nyquist frequency. Theoretically it is possible to reconstruct the input signal with more than 2 samples per period. In practice, 10 to 20 samples per period are recommended to be able to examine the signal thoroughly |
| Softscope - Time-base | The time-base allows you to set the speed at which all the lines for each channel are drawn, and is calibrated in milliseconds per division |
| Softscope - Trace | The trace is the resulting graph of a variable's evolution against time, with the more distant past on the left and the more recent past on the right |
| Stepper Drive | A stepper drive is a special electric amplifier used to power electric stepper motors without position feedback (open-loop). It controls the current to the various phases in a stepper motor to control the motor’s position. |
| Synchronization | Combines an axis or axes group (as slave) with an axis as master so that the slave executes its path with synchronization to the progress of the master, meaning linked to a one-dimensional source for synchronization |
| SynqNet | SynqNet is a digital machine control network. Built on the 100BT physical layer, SynqNet provides a synchronous real-time connection between motion controllers, servo drives, stepper drives, I/O modules, and custom devices |
| Tag | In the HMI |
| Timestamp | A timestamp is a sequence of characters denoting the date and/or time at which a certain event occurred |
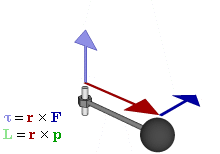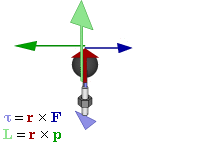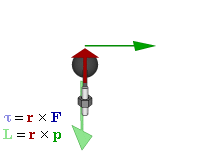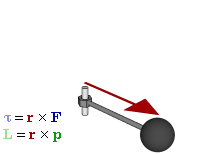
| Torque |
Torque is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist. The SI unit for torque is the newton metre (N.m). |
| Typecasting | In computer science, type conversion or typecasting refers to changing an entity of one data type into another. It is done to take advantage of certain features of type hierarchies. For instance, values from a more limited set, such as integers, can be stored in a more compact format and later converted to a different format enabling operations not previously possible, such as division with several decimal places' worth of accuracy. There are two types of conversion: implicit and explicit. The term for implicit type conversion is coercion. The most common form of explicit type conversion is known as casting. Explicit type conversion can also be achieved with separately defined conversion routines such as an overloaded object constructor |