Function
Function![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Connect a converter Pipe Block to the specified axis.
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Connect a converter Pipe Block to the specified axis.
When using the Pipe Network for coordinated motion, Pipe Blocks have to be Activated, Connected, and then Powered On before move commands work.
The Converter block changes the incoming flow of values to continuous position output with no periodicity. If a converter block is not connected to an Axis, it does not send position output values to its assigned Axis. Every pipe branch must end in a converter, whether or not it is connected to a destination Axis object, as seen in Figure 1 below.
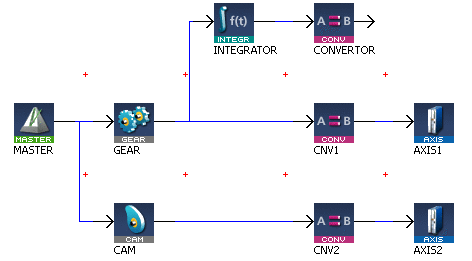
Figure 7-89: MLCNVConnect
-
-
All converters in the Pipe Network can be connected at once with the command PipeNetwork(MLPN_Connect). This calls automatically generated code with MLCNVConnect commands for each Converter block. Therefore, in a multi-axis program only one command can be used to connect Pipe Blocks instead of writing code for each Axis separately.
-
-
The converter block has the ability to control the analog output on the AKD. See for information on the parameters.
Arguments
Input
| BlockID | Description | ID number of an initiated Converter object |
| Data type | DINT | |
| Range | [-2147483648, 2147483648] | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — | |
| AxisID | Description | ID number of an initiated Axis object |
| Data type | DINT | |
| Range | [-2147483648, 2147483648] | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — |
Output
| Default (.Q) | Description | Returns TRUE if the converter is connected to the Axis objectSee Function - General Rules for more information. |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| Unit | N/A |
Return Type
BOOL
Related Functions
Example
Structured Text
//Connect a converter Pipe Block named “CNV1” to Pipe Block AXIS1
MLCNVConnect( PipeNetwork.CNV1, AXIS1 );
Ladder Diagram

Function Block Diagram