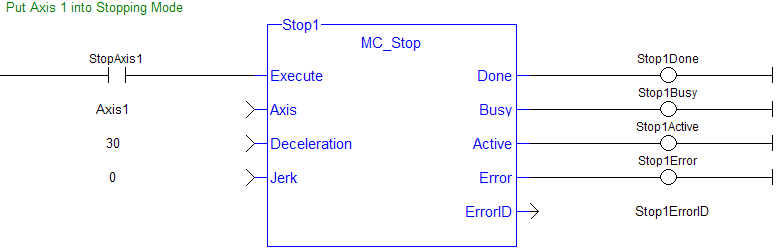
MC_Stop
MC_Stop
Description
MC_Stop cannot be aborted. This means that, while in Stopping state, no function block can command any motion on the axis. The axis remains in Stopping state until it reaches zero velocity and the Execute input is low. The application program can hold the axis in Stopping state even after it reaches zero velocity by leaving the Execute input high.
Figure 7-126: MC_Stop
Time Diagram
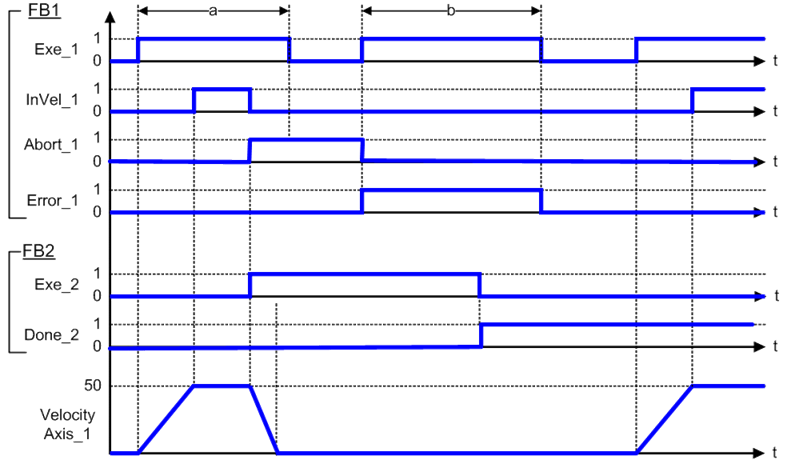
The example below shows the behavior of the combination of a MC_Stop FB with a MC_MoveVelocity FB.
- A rotating axis is ramped down with FB2 MC_Stop
- The axis rejects motion commands as long as MC_Stop parameter “Execute” = TRUE
FB1 MC_MoveVelocity reports an error indicating the busy MC_Stop command.

-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and therefore stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
Arguments
See Function Blocks - General Rules for more information about how inputs and outputs work.
Input
| Execute | Description | Requests to stop the axis. It can be held high to prevent any other moves from being queued |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0, 1 | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — | |
| Axis | Description | Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function. For more details, Axis Name and Number |
| Data type | AXIS_REF | |
| Range | [1,256] | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — | |
| Deceleration | Description | Trapezoidal: Deceleration rate S-curve: Maximum deceleration |
| Data type | LREAL | |
| Range | — | |
| Unit | User unit/sec2 | |
| Default | — | |
| Jerk |
Description | Trapezoidal: 0 S-curve: Constant jerk |
| Data type | LREAL | |
| Range | — | |
| Unit | User unit/sec3 | |
| Default | — |
Output
| Done | Description | Indicates the axis has reached zero velocity AND the Execute input is low |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| Busy | Description | High from the time the Execute input goes high until the axis reaches zero velocity AND the Execute input is low |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| Active | Description | High from the time the MC_Stop move becomes the active move, until the axis reaches zero velocity AND the Execute input is low |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| Error | Description | Indicates an invalid input was specified |
| Data type | BOOL | |
| ErrorID | Description | Indicates the error if Error output is set to TRUE |
| Data type | INT |
Example
Structured Text
(* MC_Stop S
T example *)
Inst_MC_Stop( StopRequest , Axis1, 100.0, 100.0 ); //Inst_MC_Stop is an instance of MC_Stop function block
StopComplete := Inst_MC_Stop.Done; //store the Done output into a user defined variable
StopActive := Inst_MC_Stop.Active; //store the Active output into a user defined variable
StopError := Inst_MC_Stop.Error; //store the Error output into a user defined variable
Ladder Diagram