![]()
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IN |
BOOL |
|
|
|
Boolean value. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
BOOL |
|
|
Boolean negation of the input. |
Truth Table
|
IN |
Q |
|---|---|
|
0 |
1 |
|
1 |
0 |
Remarks
FBD Language
- In the FBD
 "Function block diagram"
A function block diagram describes a function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks language, the block "NOT" can be used.
"Function block diagram"
A function block diagram describes a function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks language, the block "NOT" can be used. - Alternatively, you can use a link terminated by a "o" negation.
Example: Explicit use of the NOT block:
Example: Use of a negated link: Q is IN1 AND NOT IN2:
FFLD Language
- In the FFLD language, negated contacts and coils can be used.
Example: Negated contact: Q is: IN1 AND NOT IN2: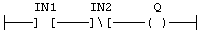
Example: Negated coil: Q is NOT (IN1 AND IN2):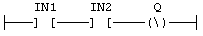
IL Language
- In the IL
 "Instruction list"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly language, the N modifier can be used with instructions FFLD, AND, OR, XOR and ST
"Instruction list"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly language, the N modifier can be used with instructions FFLD, AND, OR, XOR and ST "Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal.
"Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal. - It represents a negation of the operand.
Op1: FFLDN IN1
OR IN2
ST Q (* Q is equal to: (NOT IN1) OR IN2 *)
Op2: FFLD IN1
AND IN2
STN Q (* Q is equal to: NOT (IN1 AND IN2) *)st
ST Language
- In the ST language, NOT can be followed by a complex Boolean expression between parentheses.
Q := NOT IN;
Q := NOT (IN1 OR IN2);
See Also






