![]()
![]()
 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Commands interpolated linear movement on an axes group to the specified absolute positions
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Commands interpolated linear movement on an axes group to the specified absolute positions![]() Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different..
Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different..
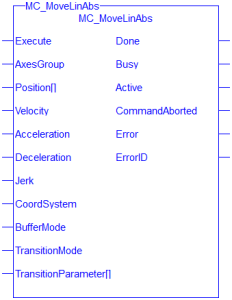
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
AxesGroup |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
The axis group that performs the linear absolute move. |
|
|
Position[] |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Array of absolute end positions for each axis in the group. |
|
LREAL |
User unit/sec |
No default |
Maximum velocity of the defined path |
||
|
Acceleration |
LREAL |
0 < Velocity < (20 * Acceleration) |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Maximum acceleration. |
|
Deceleration |
LREAL |
0 < Velocity < (20 * Deceleration) |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Maximum deceleration. |
|
Jerk |
LREAL |
Trapezoidal velocity profiles: S-Curve velocity profiles: |
User unit/sec3 |
No default |
Maximum jerk. |
|
CoordSystem |
SINT |
One of these enumeration values:
|
N/A |
No default |
The coordinate system used when commanding the linear absolute move.
|
|
BufferMode |
SINT |
One of these enumeration values:
|
N/A |
No default |
Defines the chronological sequence of the function
|
|
TransitionMode |
SINT |
The value is limited to:
|
N/A |
No default |
Coupled with the TransitionParameter[ ], this input defines the shape and dynamics of the inserted contour to connect the current motion with the next motion in the queue.
|
|
TransitionParameter[ ] |
LREAL |
1, N |
N/A |
No default |
This array is dependent on the specified TransitionMode.
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Done |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
If TRUE, the command completed successfully. |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
If TRUE, the function block is executing. |
|
Active |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
If TRUE, the function block is controlling motion. |
|
CommandAborted |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
If TRUE, the command was aborted by another function block. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
If TRUE, an error has occurred. |
|
ErrorID |
INT |
-32768 to +32767 |
N/A |
Indicates the error if Error output is TRUE. |
Remarks
- See Coordinated Motion, the top-level topic for Coordinated Motion.
- When all motion has completed successfully, the axes group state is GroupStandby.
- MC_MoveLinAbs commands interpolated linear movement on an axes group to the specified absolute positions in the coordinate system as specified by the CoordSystem argument.
- The dimensionality of the move is determined by the number of axes mapped to the group.
-
-
- An error is returned if the group is in the GroupDisabled state.
- The maximum number of axes is set by the MaxNumberOfAxes input set in the MC_CreateAxesGrp function block.
-
-
- Circular motion is only supported for axes groups with only two attached axes.
Figure 1: MC_MoveLinAbs
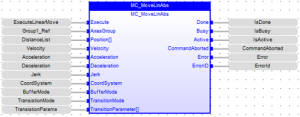
FBD Language Example
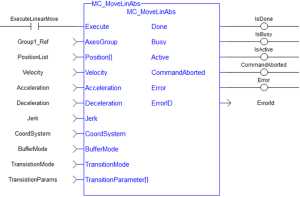
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
BEGIN_IL Instruction list - This is a low-level language and resembles assembly.
CAL Inst_MC_MoveLinAbs( ExecuteLinearMove, Group1_Ref, PositionList, Velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, Jerk, CoordSystem, BufferMode, TransitionMode, TransitionParams )
Instruction list - This is a low-level language and resembles assembly.
CAL Inst_MC_MoveLinAbs( ExecuteLinearMove, Group1_Ref, PositionList, Velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, Jerk, CoordSystem, BufferMode, TransitionMode, TransitionParams )
END_IL
ST Language Example
(* Inst_MC_MoveLinAbsST example *)
Inst_MC_MoveLinAbs( ExecuteLinearMove, Group1_Ref, PositionList, Velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, Jerk, CoordSystem, BufferMode, TransitionMode, TransitionParams );
See Also