![]()
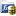 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Computes the derivative of a signal with respect to time.
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Computes the derivative of a signal with respect to time.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RUN |
BOOL |
TRUE, FALSE |
|
|
Run command:
|
|
XIN |
REAL |
|
|
|
Input signal. |
|
CYCLE |
TIME |
|
|
|
Must not be less than the target cycle timing. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XOUT |
REAL |
|
|
Output signal. |
Remarks
- The time unit is seconds.
- The output signal has the units of the input signal divided by seconds.
- The derivate block samples the input signal at a maximum rate of 1 millisecond.
FBD Language Example
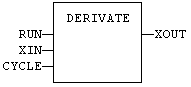
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD Language, the input rung is the RUN command.
- The output rung keeps the state of the input rung.
- ENO has the same state as RUN.
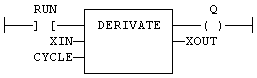
IL Language Example
(* MyDerv is a declared instance of DERIVATE functionA function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. block *)
Op1: CAL MyDerv (RUN, XIN, CYCLE)
FFLD MyDerv.XOUT
STStructured text - A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal. XOUT
ST Language Example
(* MyDerv is a declared instance of DERIVATE function block. *)
MyDerv (RUN, XIN, CYCLE);
XOUT := MyDerv.XOUT;
See Also






