Motion Control Main Functions
![]() Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different. and movement, motion control
Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different. and movement, motion control![]() Motion control is a sub-field of automation, in which the position and/or velocity of machines are controlled using some type of device such as a hydraulic pump, linear actuator, or an electric motor, generally a servo.
Motion control is an important part of robotics and CNC machine tools.
However, it is more complex than in the use of specialized machines, where the kinematics are usually simpler.
The latter is often called General Motion Control (GMC).
Motion control is widely used in the packaging, printing, textile, and assembly industries consists of the two following main parts:
Motion control is a sub-field of automation, in which the position and/or velocity of machines are controlled using some type of device such as a hydraulic pump, linear actuator, or an electric motor, generally a servo.
Motion control is an important part of robotics and CNC machine tools.
However, it is more complex than in the use of specialized machines, where the kinematics are usually simpler.
The latter is often called General Motion Control (GMC).
Motion control is widely used in the packaging, printing, textile, and assembly industries consists of the two following main parts:
- Setpoint
 The target value that an automatic control system (e.g., PID controller) aims to reach. generation
The target value that an automatic control system (e.g., PID controller) aims to reach. generation - Regulation
Setpoint Generation
- This consists of generating a trajectory
 Time dependent description of the path the TCP of an axes group moves along.
Additional to the geometrical description of the space curve, time dependent state variables like velocity, acceleration, jerk, forces etc. are specified. defined by position versus time.
Time dependent description of the path the TCP of an axes group moves along.
Additional to the geometrical description of the space curve, time dependent state variables like velocity, acceleration, jerk, forces etc. are specified. defined by position versus time. - It is purely logical and does not relate to the physical world.
Regulation
Even using the very best drives![]() In electrical engineering, a drive is an electronic device to provide power to a motor or servo.
Control device for regulating the speed, torque and position of a motor.
A unit controlling a motor using the current and timing in its coils., you cannot maintain accurate positioning without a feedback loop.
In electrical engineering, a drive is an electronic device to provide power to a motor or servo.
Control device for regulating the speed, torque and position of a motor.
A unit controlling a motor using the current and timing in its coils., you cannot maintain accurate positioning without a feedback loop.
- The regulation consists of following the generated position settings using classical feed-forward
 This describes an element or pathway within a control system which passes a controlling signal from a source in the control system's external environment, often a command signal from an external operator, to a load elsewhere in its external environment. or feedback control-loops (by means of PID
This describes an element or pathway within a control system which passes a controlling signal from a source in the control system's external environment, often a command signal from an external operator, to a load elsewhere in its external environment. or feedback control-loops (by means of PID Proportional-Integral-Derivative - A PID controller is a generic control-loop feedback mechanism widely used in industrial control systems.
An error occurs when an event or a disturbance triggers off a change in the process variable.
A PID controller attempts to correct the error between a measured process variable and a desired setpoint by calculating and then outputting a corrective action that can adjust the process accordingly.).
Proportional-Integral-Derivative - A PID controller is a generic control-loop feedback mechanism widely used in industrial control systems.
An error occurs when an event or a disturbance triggers off a change in the process variable.
A PID controller attempts to correct the error between a measured process variable and a desired setpoint by calculating and then outputting a corrective action that can adjust the process accordingly.). - See How do I implement feedback? for more information.
- Regulation is the part which takes care of the physical world of making moving motors
 An actuator focused to a movement, converting electrical energy in a force or torque..
An actuator focused to a movement, converting electrical energy in a force or torque..
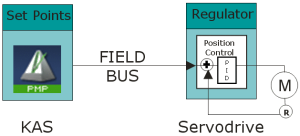
These two functions![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs.
A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. can be located on the same hardware (as in a "stand-alone" servo drive
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs.
A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. can be located on the same hardware (as in a "stand-alone" servo drive![]() A special electric amplifier used to power electric servo motors.
It monitors feedback signals from the motor and continually adjusts for deviation from expected behavior.) or on two separate hardware devices, linked together by a fieldbus
A special electric amplifier used to power electric servo motors.
It monitors feedback signals from the motor and continually adjusts for deviation from expected behavior.) or on two separate hardware devices, linked together by a fieldbus![]() An industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g., CAN or PROFIBUS, Sercos®).
It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design..
An industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g., CAN or PROFIBUS, Sercos®).
It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design..