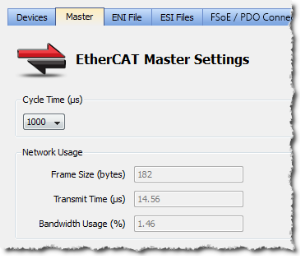
EtherCAT Master Settings tab
This tab includes configurations for the EtherCAT![]() Ethernet ofr Control Automation Technology.
EtherCAT® is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system.
The development goal of EtherCAT is to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs. bus master.
Ethernet ofr Control Automation Technology.
EtherCAT® is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system.
The development goal of EtherCAT is to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs. bus master.
Figure 1: EtherCAT Master Settings
The read-only fields show (unknown) when the Use imported file check box is selected.
Otherwise, they are recalculated and refreshed![]() GUI command that re-loads the data from the drive and redraws the display. each time:
GUI command that re-loads the data from the drive and redraws the display. each time:
- A device is added or removed.
- A device simulation state changes.
- See EtherCAT Devices tab for more information.
- The Use imported file check box is cleared.
See ENI File tab for more information.
Bandwidth Calculation Algorithm
The Bandwidth (BW) usage calculation takes into account the calculated frame size and the Ethernet![]() Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs). speed
Ethernet is a large, diverse family of frame-based computer networking technologies that operate at many speeds for local area networks (LANs). speed![]() Speed is the absolute value of the velocity without direction. (100 Megabits per second).
Speed is the absolute value of the velocity without direction. (100 Megabits per second).
BW% = Transmission time / Cycle Time
With Transmission time (μsec) = (Frame Size in bytes * 8) bits / 100 * 106 bps
Example
If Frame Size = 100 bytes
then Transmission Time = 100*8 / (100*106 ) = 8 μsec
If cycle time = 1000 μsec
then BW% = 8/1000 = 0.8 %