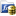 TcpIsConnected
TcpIsConnected
Description
This function block tests if a client socket is connected.
-
- It is possible that the socket becomes invalid if an error occurs in the TCP connection after this function block is called. You must use the TcpIsValid function block after TcpSend. If the socket is no longer valid then you must close it by using the TcpClose function block.

Figure 7-222: The TcpIsConnected function block
Related Functions
TcpAccept, TcpBinReceive, TcpBinSend, TcpClose, TcpConnect, TcpIsConnected, TcpIsValid, TcpListen, TcpReceive, TcpSend
Arguments
Input
| Execute | Description | On the rising edge |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0, 1 | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — | |
| ID | Description | ID of the client socket |
| Data Type | UDINT | |
| Range | N/A | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | — |
Output
| Done | Description | If TRUE, then the command completed successfully |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Error | Description | If TRUE, an error has occurred |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| ErrorID | Description | Indicates the error if Error output is set to TRUE. See the table in Search IndexFile and TCP/IP Function Block ErrorID Output |
| Data Type | DINT | |
| Connected | Description | TRUE if connection is correctly established. |
| Data Type | BOOL |
Example
Structured Text
(* TcpIsConnected example *)
CASE StepCounter OF
0:
Inst_TcpIsConnected(TRUE, MySocketID);
StepCounter := StepCounter + 1;
1:
Inst_TcpIsConnected(TRUE, MySocketID);
IF Inst_TcpIsConnected.Done THEN
MyTcpIsConnected := Inst_TcpIsConnected.Connected;
Inst_TcpIsConnected(FALSE, 0);
StepCounter := StepCounter + 1;
END_IF;
END_CASE;






