![]()
![]()
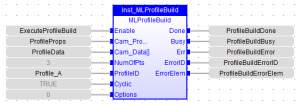
This Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. allows the application to create a cam profile that may be executed by a cam block in PipeNetwork or PLCopen
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. allows the application to create a cam profile that may be executed by a cam block in PipeNetwork or PLCopen![]() A vendor -and product- independent worldwide association active in Industrial Control and aiming at standardizing PLC file formats based on XML.
A vendor -and product- independent worldwide association active in Industrial Control and aiming at standardizing PLC file formats based on XML.
This Function Block will take input as cam data (see Cam Profile Editor's Cam Table for information) and profile properties from application data memory and compile the input data to a form the controller can use to calculate cam positions. The input cam data and profile properties are similar to the cam data entered in the IDE![]() "Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger’s Cam Editor and the runtime
"Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger’s Cam Editor and the runtime![]() In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running’s Cam Profile Properties dialog. MLProfileBuild internally perform two functions:
In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running’s Cam Profile Properties dialog. MLProfileBuild internally perform two functions:
- Compile the cam data (like the cam editor performs in the IDE).
- Puts the compiled profile into the profile object so it can be used by other Profile Function Blocks (provides similar functionality to MLProfileInit).
-
-
Prior to using MLProfileBuild you must call MLProfileCreate to create the profile object. The
IDoutput of MLProfileCreate is then used as theProfileIDinput to MLProfileBuild. MLProfileCreate must be performed in the application before the MLMotionStart command is executed.
MLProfileBuild will compile the cam profile data specified at the CamData input and write the resulting profile to the CAM Profile object specified at input ProfileID. The created profile can then be used as an input to PLCopen Cam Function Blocks (MC_CamTblSelect, MC_CamIn, MC_CamOut), or any Pipe network Cam Profile Function/Function Blocks. When the operation is complete, the Done output will go high. If an error is encountered, the Error output will go high and the ErrorID output will return a error code. If the Error can be attributed to a specific profile element in the CamData array, ErrorElem will attempt to indicate the element in error.
CamProps_Ref Structure
The cam properties structure (CamProps_Ref) will contain the following data members:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| InputScale | LREAL | The input amplitude or master axis multiplier applied to the CAM profile |
| OutputScale | LREAL | The output amplitude or slave axis multiplier applied to the CAM profile |
| InputOffset | LREAL | input offset or master axis shift applied to the CAM profile |
| OutputOffset | LREAL | The output offset or slave axis shift applied to the CAM profile |
See Master/Input offset for more information about the parameters which transform the cam profile.
CamData_Ref Structure
The Cam_Data function block input will be an array of CamData_Ref structures. Each element of the structure will contain the following data members:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MasterIn | LREAL | master position (in the unit range [0 - InputScale]) |
| SlaveOut | LREAL | slave position (in the unit range [0 - OutputScale]) |
| SegType | UINT |
Defines the segment type for the segment following the master positions defined by MasterIn.
See Cam Profile Segment Overview for information on the segment types. |
| Vel | LREAL | Cam velocity at the master position specified by MasterIn. Units: (slave position user units) / (master position user units) |
| Accel | LREAL |
For CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_POINT: Accel represents the cam acceleration at the master position specified by MasterIn. Units: For CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_LINE and CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC: Accel is ignored. |
The type of the Nth cam segment is defined by the Nth Cam_Data element. Since the cam will be constructed with one les segment than the Cam_Data elements, the last element's SegType will not be used.
See Cam Profile Editor's Cam Table for more information.
Arguments
Input
|
Enable |
Description | Enable execution. Starts on rising edge |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | ||
| Unit | ||
| Default | ||
|
Cam_Props |
Description | Structures containing the cam profile properties |
| Data Type | CamProps_ref | |
| Range | ||
| Unit | ||
| Default | ||
|
Cam_Data |
Description | Array of structures containing the cam profile data |
| Data Type | CamData_ref | |
| Range | N=3 to 20,000 elements | |
| Unit | ||
| Default | 3 elements minimum size | |
|
CamDataCount |
Description | Number of elements in the Cam_Data array to be used. |
| Data Type | UINT | |
| Range | 3 - 20,000 | |
| Unit | elements | |
| Default | 3 | |
|
ProfileID |
Description | ID number of a created CAM Profile |
| Data Type | DINT | |
| Range | [-2147483648, 2147483648] | |
| Unit | N/A | |
| Default | -- | |
|
Cyclic |
Description | False: one time through the profile; True: repeating profile |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0-1 (FALSE/TRUE) | |
| Unit | ||
| Default | ||
|
Options |
Description | Describes the combinations of segments that may be used to build a cam profile. |
| Data Type | UINT | |
| Range | CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_DEFAULT: Allows the use of point and line segments. CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_PARABOLIC: Allows the use of line and parabolic segments.
|
|
| Unit | ||
| Default |
Output
|
Done |
Description | Indication of whether or not the profile was successfully compiled and built. |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0-1 (FALSE/TRUE) | |
| Unit | ||
|
Busy |
Description | Indication that the function block is executing. TRUE if executing. False if not executing. |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0-1 (FALSE/TRUE) | |
| Unit | ||
|
Err |
Description | Indication that the function did not execute correctly. ErrorID output will be valid and indicate the reason. |
| Data Type | BOOL | |
| Range | 0-1 (FALSE/TRUE) | |
| Unit | ||
|
ErrorID |
Description | Indication of the reason for the failure to execute properly. See Error Codes table. |
| Data Type | INT | |
| Range | ||
| Unit | ||
|
ErrorElem |
Description | The array element number of the cam data where an error is detected |
| Data Type | UINT | |
| Range | ||
| Unit |
Error Codes
-
-
If Cyclic is TRUE and the Vel/Accel of the first and last elements do not match, MLProfileBuild will automatically copy the first element's vel/accel to the last element's. A LOG warning message will be posted indicating that this change has occurred.
| ErrorID | Description |
|---|---|
| 100 | Cam_Data array does not have CamDataCount elements. The Cam_Data array is not large enough to hold the specified number of elements. |
| 101 | Invalid master or slave scale. The scale cannot be less than zero. |
| 102 | Element master or slave position is outside the range defined by Cam_Props. |
| 103 | A segment type was specified that is not supported by the value of the Options argument. |
| 104 | Master position of an element is too close to the master position of a previous element. 0.0000125 * InputScale (see "CamProps_Ref Structure") is the minimum distance allowed.. Each element is compared to all previous elements. If the master distance between any two elements in the list are too close, this error will be generated. |
| 106 | Invalid profile ID. This can occur if the profile ID:
|
| 107 | CamDataCount exceeds maximum array size of 20,000. |
| 108 | Profile is currently in use. |
| 109 | Attempting to build a profile already containing elements. Profile needs to be released first using MLProfileRelease. |
| 110 | The controller is running low on memory and could not allocate memory to hold the cam table data. |
| 111 | CamDataCount is not large enough. The minimum allowed value is 3. |
| 112 | For CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_PARABOLIC: Elements are not sorted in increasing order by master position. After the first elelment, each element must have its master position be greater than the master position of the previous element. |
| 113 | For CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC: The average velocity for the segment is outside of range defined by start and end element velocities. The following diagram illustrates the valid range for the average velocity.  |
| 200 | First element's MasterIn value not equal to zero. |
| 201 | Last element's MasterIn value does not equal value of X-amplitude. |
| 202 | Cannot modify the first element in the cam element table. SlaveOut value is outside the output range specified by Cam_Props. |
| 203 | Cannot modify the last element in the cam element table. SlaveOut value is outside the output range specified by Cam_Props. |
Related Functions
- MLCamInit
- MLCamSwitch
- MLProfileCreate
- MLProfileInit
- MLProfileRelease
- MC_CamIn
- MC_CamOut
- MC_CamTblSelect
See Also
Example of How to Use MLProfileBuild
Prior to using MLProfileBuild you must first create a profile. This must be done prior to MLMotionStart.
// Allocate space for a profile that will be built later
profileID := MLProfileCreate('ProfileName');
Next you need to define your profile data. This is done by creating an array of CamData_Ref structures in the data dictionary and then entering each of your elements into that newly created structure. In this example ProfileData is the name of the CamData_Ref structure.
// Define the profile data
ProfileData[0].MasterIn := 0.0;
ProfileData[0].SlaveOut := 180.0;
ProfileData[0].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_POINT;
ProfileData[0].Velocity := 0.0;
ProfileData[0].Acceleration := 0.0;
ProfileData[1].MasterIn := 180.0;
ProfileData[1].SlaveOut := 324.0;
ProfileData[1].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_POINT;
ProfileData[1].Velocity := 0.5;
ProfileData[1].Acceleration := -0.025;
ProfileData[2].MasterIn := 360.0;
ProfileData[2].SlaveOut := 240.0;
ProfileData[2].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_POINT;
ProfileData[2].Velocity := 0.0;
ProfileData[2].Acceleration := 0.0;
Now you need to define your profile properties. This is done by creating a CamProps_Ref structure in the data dictionary and then entering each of the properties into the newly created structure. In this example ProfileProps is the name of the CamProps_Ref structure.
// Define the profile properties
ProfileProps.InputScale := 360.0; // Must be Positive!
ProfileProps.OutputScale := 360.0; // Must be Positive!
ProfileProps.InputOffset := 0.0;
ProfileProps.OutputOffset := 0.0;
Next call the MLProfileBuild Function Block in the IEC![]() "International Electrotechnical Commission"
IEC is a not-for-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies language of choice. As part of this call it is recommended that you validate the
"International Electrotechnical Commission"
IEC is a not-for-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies language of choice. As part of this call it is recommended that you validate the Done and Error output before proceeding.
// Build the profile
Inst_MLProfileBuild( TRUE, ProfileProps, ProfileData, 3, ProfileID, TRUE, CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_DEFAULT);
Finally, after verifying that MLProfileBuild is Done and there are no errors, you can proceed and use the newly generated profile. The next step depends on the motion engine in use.
- PLCopen: call MC_CamTblSelect
- Pipe Network: call either MLCamInit or MLCamSwitch
-
- Pipe Network: In order to correctly set the cam scales and offsets (defined by the Cam_Props argument) MLPrfWriteIScale, MLPrfWriteOScale, MLPrfWriteIOffset and MLPrfWriteOOffset must be called before calling MLCamSwitch,
// Switch Pipe Network Profile
MLPrfWriteIScale(profileID, ProfileProps.InputScale);
MLPrfWriteOScale(profileID, ProfileProps.OutputScale);
MLPrfWriteIOffset(profileID, ProfileProps.InputOffset);
MLPrfWriteOOffset(profileID, ProfileProps.OutputOffset);
MLCamSwitch(PipeNetwork.CAM, profileID);
Example of Building a Parabolic Cam Profile
In order to build a parabolic cam profile, your cam data elements must use CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC or CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_LINE when defining the cam data array:
// Define the profile data
ProfileData[0].MasterIn := 0.0;
ProfileData[0].SlaveOut := 0.0;
ProfileData[0].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC;
ProfileData[0].Velocity := 0.0;
ProfileData[0].Acceleration := 0.5;
ProfileData[1].MasterIn := 50.0;
ProfileData[1].SlaveOut := 150.0;
ProfileData[1].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_LINE;
ProfileData[1].Velocity := 5.0;
ProfileData[1].Acceleration := 0.0; // Not used
ProfileData[2].MasterIn := 55.0;
ProfileData[2].SlaveOut := 175.0;
ProfileData[2].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC;
ProfileData[2].Velocity := 5.0;
ProfileData[2].Acceleration := 0.0; // No limit to the acceleration rate of the segment.
ProfileData[3].MasterIn := 105.0;
ProfileData[3].SlaveOut := 250.0;
ProfileData[3].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC;
ProfileData[3].Velocity := 0.0;
ProfileData[3].Acceleration := 0.5;
ProfileData[4].MasterIn := 225.0;
ProfileData[4].SlaveOut := 125.0;
ProfileData[4].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC;
ProfileData[4].Velocity := -10.0;
ProfileData[4].Acceleration := 0.5;
ProfileData[5].MasterIn := 360.0;
ProfileData[5].SlaveOut := 0.0;
ProfileData[5].SegType := CAM_SEGMENT_TYPE_PARABOLIC; // Not used
ProfileData[5].Velocity := 0.0;
ProfileData[5].Acceleration := 0.0; // Not used
When calling the MLProfileBuild function block, make sure CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_PARABOLIC is specified for the Option argument: in the IEC language of choice. As part of this call it is recommended that you validate the Done and Error output before proceeding.
// Build the profile
Inst_MLProfileBuild( TRUE, ProfileProps, ProfileData, 3, ProfileID, TRUE, CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_PARABOLIC);
Code Examples
Structured Text:
// Build the profile
Inst_MLProfileBuild( TRUE, ProfileProps, ProfileData, 3, ProfileID, TRUE, CAM_PROFILE_OPTION_DEFAULT);
Function Block Diagram:
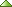
Ladder Diagram: