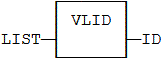![]()
 Function
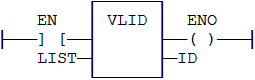
Function![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Gets the identifier (ID) of an embedded list of variables.
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Gets the identifier (ID) of an embedded list of variables.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
FILE |
STRING |
|
|
|
Pathname of the list file (.SPL or .TXT). Must be a constant value. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ID |
DINT |
|
|
ID of the list. To be passed to other blocks. |
Remarks
-
-
List files are read at compiling time and are embedded into the downloaded application code.
This implies that a modification performed in the list file after downloading is not taken into account by the application.
- This function is used to create an Identifier (ID) or ListID for a list of application variables that are typically stored on the development PC.
- The list of application variables:
- Is a simple .TXT file.
- Can contain only one variable name per line.
- Can be only global variables (i.e., Internal variables known by all programs.)
- This function's ID output can be used as an input to LogFileCSV.
- It defines the application variables whose present value is recorded each time LogFileCSV is executed.
FBD Language Example
FFLD Language Example
- The function is executed only if EN is TRUE.
IL Language Example
Op1: LD"Ladder diagram" Ladder logic is a method of drawing electrical logic schematics. It is now a very popular graphical language for programming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). It was originally invented to describe logic made from relays. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical "rails" and a series of horizontal "rungs" between them 'MyFile.txt'
VLID COL
ST ListID
ST Language Example
ID := VLID ('MyFile.spl');