Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IN1 |
ANY_NUM |
|
|
|
First input. |
|
IN2 |
ANY_NUM |
|
|
|
Second input. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
ANY_NUM |
|
|
Result: IN1 * IN2. |
Remarks
- All inputs and the output must have the same type.
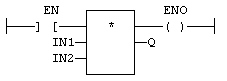
FBD Language Example
- In the FBD
 "Function Block Diagram"
A function block diagram describes a function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks Language, the block can have a maximum of 32 inputs.
"Function Block Diagram"
A function block diagram describes a function between input variables and output variables. A function is described as a set of elementary blocks Language, the block can have a maximum of 32 inputs.
FFLD Language Example
- The multiplication is executed only if EN is TRUE.
- In the FFLD
 "Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.
"Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.- The output rung (ENO) keeps the same value as the input rung.
- ENO is equal to EN.
IL Language Example
- In the IL
 "Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly Language, the MUL instruction performs a multiplication between the current result and the operand.
"Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly Language, the MUL instruction performs a multiplication between the current result and the operand. - The current result and the operand must have the same type.
Op1: FFLD IN1
MUL IN2
ST Q (* Q is equal to: IN1 * IN2 *)
Op2: FFLD IN1
MUL IN2
MUL IN3
ST Q (* Q is equal to: IN1 * IN2 * IN3 *)
ST Language Example
Q := IN1 * IN2;
See Also