![]()
 Function
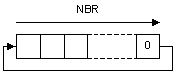
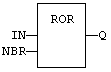
Function![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Rotate bits of a register to the right.
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Rotate bits of a register to the right.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IN |
ANY |
|
|
|
Register. |
|
NBR |
ANY |
|
|
|
Number of rotations (each rotation is 1 bit). |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
ANY |
|
|
Rotated register. |
Remarks
- Arguments can be signed or unsigned integers from 8- to 32-bits.
Diagram
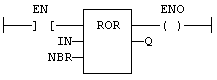
FBD Language Example
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD
 "Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.
"Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.- The output rung keeps the state of the input rung.
- The rotation is executed only if EN is TRUE.
- ENO keeps the same value as EN.
IL Language Example
- In the IL
 "Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly Language, the first input must be loaded before the function call.
"Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly Language, the first input must be loaded before the function call.- The second input is the operand of the function.
Op1: LD"Ladder diagram" Ladder logic is a method of drawing electrical logic schematics. It is now a very popular graphical language for programming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). It was originally invented to describe logic made from relays. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical "rails" and a series of horizontal "rungs" between them IN
ROR NBR
ST Q
ST Language Example
Q := ROR (IN, NBR);
See Also