EtherNet/IP Adapter (Server)
The KAS Runtime![]() In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running includes fully integrated EtherNet/IP server driver for exchanging CIP
In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running includes fully integrated EtherNet/IP server driver for exchanging CIP![]() "Common Industrial Protocol "
The Common Industrial Protocol allows complete integration of control with information, multiple CIP Networks, and Internet technologies I/O assemblies as an EtherNet/IP adapter in your applications.
"Common Industrial Protocol "
The Common Industrial Protocol allows complete integration of control with information, multiple CIP Networks, and Internet technologies I/O assemblies as an EtherNet/IP adapter in your applications.
Data Exchange - Configuration
A dedicated configuration tool is integrated in the KAS-IDE![]() "Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger.
"Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger.
- Double-click the Fieldbus
 A Fieldbus is an industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g. CAN or Profibus). It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design node in the project explorer to open it.
A Fieldbus is an industrial network system for real-time distributed control (e.g. CAN or Profibus). It is a way of connecting instruments in a plant design node in the project explorer to open it. - Click the Insert Configuration icon
 to add the Fieldbus configuration.
to add the Fieldbus configuration. - Select the EtherNet/IP Adapter in the configuration selector.
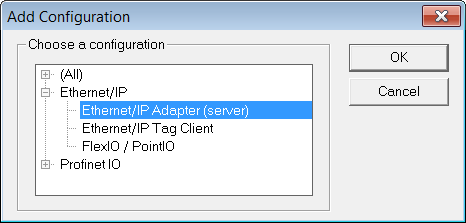
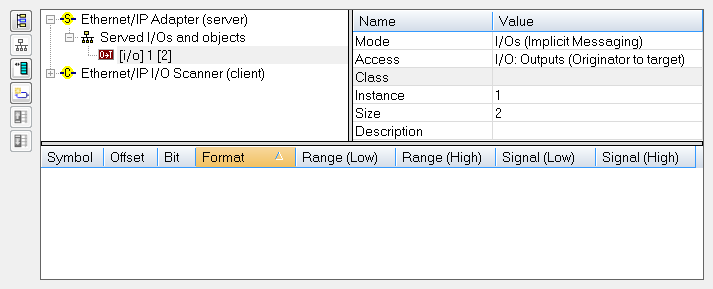
The configuration is represented as a tree:
- EtherNet/IP I/O Scanner
- Served I/Os and objects
- I/O Assembly or Vendor Specific Object (*)
- Exchanged Variable (*)
- I/O Assembly or Vendor Specific Object (*)
(*) The items with this mark can appear several times in the configuration.
- Served I/Os and objects
Configuration
These items can be configured at the root level:
| Identifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
Use LAN2 |
Obsolete |
|
IP Address |
IP address of the Ethernet |
Click the Insert Master icon  to declare a server (adapter device). Each server is identified by its IP address and an optional description text.
to declare a server (adapter device). Each server is identified by its IP address and an optional description text.
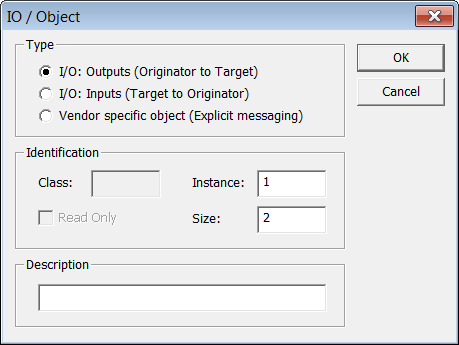
Select the Served I/Os and objects node, then click the Insert Slave icon  to declare a CIP I/O assembly or a vendor specific object. Up to 4 input and 4 output assemblies are supported by the KAS Runtime, even though it is possible to create more in the KAS-IDE.
to declare a CIP I/O assembly or a vendor specific object. Up to 4 input and 4 output assemblies are supported by the KAS Runtime, even though it is possible to create more in the KAS-IDE.
Each assembly is identified by:
| Identifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
Mode |
The kind of CIP object. Can be one of:
|
|
Access |
In case of a vendor specific object, this property defines the access rights:
|
|
Class |
CIP class in case of a vendor specific object. This field should be ignored in case of an I/O assembly. |
|
Instance |
Instance of the CIP assembly or object. |
|
Size |
Data size in bytes. |
|
Read Only |
Specify that a vendor-specific object is only readable by clients. |
|
Description |
Optional description text. |
When defining a vendor specific objects, these attributes are available for scanners:
- 1 (get only) = size of the object data
- 3 (get/set) = object data
Then map IEC61131-3![]() IEC 61131-3 is the third part of the open international standard IEC 61131. The current (second) edition was published in 2003.
IEC 61131-3 currently defines five programming languages for programmable control systems
It deals with programming languages and defines two graphical and two textual PLC programming language standards variables on the data of the assembly, for each variable you must specify:
IEC 61131-3 is the third part of the open international standard IEC 61131. The current (second) edition was published in 2003.
IEC 61131-3 currently defines five programming languages for programmable control systems
It deals with programming languages and defines two graphical and two textual PLC programming language standards variables on the data of the assembly, for each variable you must specify:
| Identifier | Meaning |
|---|---|
|
Symbol |
The name of the IEC61131 |
|
Offset |
Offset in bytes in the assembly data |
|
Bit |
Bit offset in the selected byte if format is "Bit" |
|
Format |
Format of the data in the assembly |
-
-
Drag a variable from the Dictionary directly to a slave item.
-
-
The data limit is: 500 bytes of data maximum O(originator)->T(target) and 500 bytes of data maximum T(target) -> O(originator).
This is based on the Ethernet/IP specification.