Interpret a Timestamp
The timestamp![]() A timestamp is a sequence of characters, denoting the date and/or time at which a certain event occurred is based on the EtherCAT
A timestamp is a sequence of characters, denoting the date and/or time at which a certain event occurred is based on the EtherCAT![]() ***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs system time.
***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs system time.
For this value to make sense, the distributed clock must be activated in the drive (see Distributed Clock tab) and in the EtherCAT master.
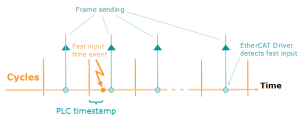
Figure 6-24: PLC Timestamp Related to Fast Input Event
- The timestamp returned is relative to the beginning of the cycle in which the Fast Input
 The inputs are taken into account at each cycle depending on the system periodicity (for example each millisecond). Under certain circumstances this can be insufficient when more accuracy is needed, or if a quick response is required from the system. To fill the gap, a drive may have some Fast Input connections (generally one or two). When an event happens that triggers a Fast Input (e.g. when a sensor sends a rising edge), the detection of a signal occurs faster (which can be 1000 times more accurate than the system periodicity). Then the timestamp associated with this input can be provided to the IPC to take corrective action is triggered.
The inputs are taken into account at each cycle depending on the system periodicity (for example each millisecond). Under certain circumstances this can be insufficient when more accuracy is needed, or if a quick response is required from the system. To fill the gap, a drive may have some Fast Input connections (generally one or two). When an event happens that triggers a Fast Input (e.g. when a sensor sends a rising edge), the detection of a signal occurs faster (which can be 1000 times more accurate than the system periodicity). Then the timestamp associated with this input can be provided to the IPC to take corrective action is triggered. - It is called PLC
 "Programmable Logic Controller"
A Programmable Logic Controller, PLC, or Programmable Controller is a digital computer used for automation of industrial processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines.
Used to synchronize the flow of inputs from (physical) sensors and events with the flow of outputs to actuators and events timestamp because it is the value used in PLC programs.
"Programmable Logic Controller"
A Programmable Logic Controller, PLC, or Programmable Controller is a digital computer used for automation of industrial processes, such as control of machinery on factory assembly lines.
Used to synchronize the flow of inputs from (physical) sensors and events with the flow of outputs to actuators and events timestamp because it is the value used in PLC programs.