SFC Execution at Runtime
![]() "Sequential Function Chart"
It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps.
The main components of SFC are:
- Steps with associated actions
- Transitions with associated logic conditions
- Directed links between steps and transitions programs are executed sequentially within a target cycle according to the order defined when entering programs in the hierarchy tree.
"Sequential Function Chart"
It can be used to program processes that can be split into steps.
The main components of SFC are:
- Steps with associated actions
- Transitions with associated logic conditions
- Directed links between steps and transitions programs are executed sequentially within a target cycle according to the order defined when entering programs in the hierarchy tree.
- A parent SFC program is executed before its children.
- This implies that when a parent starts or stops a child, the corresponding actions in the child program are performed during the same cycle.
- In a chart, all valid transitions are evaluated first and then actions of active steps are performed.
- The chart is evaluated from the left to the right and from the top to the bottom.
Example
|
Execution order:
|
The initial steps define the initial status of the program when it is started.
- All top level (main) programs are started when the application starts.
- Child programs are explicitly started from action blocks within the parent programs.
The evaluation of transitions leads to changes of active steps, according to these rules:
- A transition is crossed if:
- Its condition is TRUE and all steps linked to the top of the transition (before) are active.
- When a transition is crossed:
- All steps linked to the top of the transition (before) are deactivated.
- All steps linked to the bottom of the transition (after) are activated.
Divergence
- All conditions are considered as exclusive, according to a left-to-right priority order.
- It means a transition is considered as FALSE if at least one of the transitions connected to the same divergence on its left side is TRUE.
Order of Action Block Execution
For a given cycle, if a transition is:
- FALSE, the N-action blocks are evaluated for all active steps waiting on that transition.
- TRUE, the P0 action blocks are evaluated for all active steps waiting on that transition, followed by the P1 and N steps for all steps waiting on that transition.
- The steps that were waiting on that transition are then marked as active.
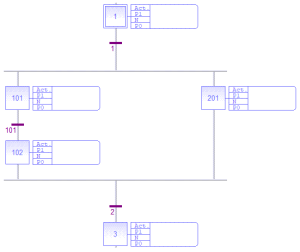
Example
Using this SFC:
The order of action block execution for a given cycle is:
|
Incoming State |
Evaluating Transition |
If Transition is FALSE |
If Transition is TRUE |
|---|---|---|---|
|
First Cycle |
N/A |
[1] P1 [1] N |
|
|
Transition 1. Not yet TRUE. |
Transition 1 |
[1] N |
[1] P0 [101] P1 [101] N [201] P1 [201] N |
|
Passed transition 1. Transition 101 not yet TRUE. |
Transition 101 |
[101] N [201] N |
[101] P0 [201] N [102] P1 [102] N |
|
Passed transitions 1 and 101 Transition 2 not yet TRUE. |
Transition 2 |
[201] N [102] N |
[201] P0 [102] P0 [3] P1 [3] N |
-
-
Execution of SFC in the IEC
 "International Electrotechnical Commission"
IEC is a not-for-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies 61131-3 target is sampled according to the target cycles.
"International Electrotechnical Commission"
IEC is a not-for-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies 61131-3 target is sampled according to the target cycles.
When a transition is crossed within a cycle, these steps are activated.
The evaluation of the chart continues in the next cycle.
If several consecutive transitions are TRUE within a branch, only one of them is crossed within one target cycle.
-
-
Some runtime
 In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running systems may not support exclusivity of the transitions within an divergence.
In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running systems may not support exclusivity of the transitions within an divergence.
See the OEM "Original equipment manufacturer"
A term that refers to containment-based re-branding, namely where one company uses a component of another company within its product, or sells the product of another company under its own brand. OEM refers to the company that originally manufactured the product instructions for more information about SFC support.
"Original equipment manufacturer"
A term that refers to containment-based re-branding, namely where one company uses a component of another company within its product, or sells the product of another company under its own brand. OEM refers to the company that originally manufactured the product instructions for more information about SFC support.