![]()
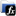 Function - Select one of the four integer inputs.
Function - Select one of the four integer inputs.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
K |
DINT |
0, 3 |
N/A |
No default |
Selection command. |
|
IN0 |
ANY |
Depends on the Data Type. |
N/A |
No default |
First input. |
|
IN1 |
ANY |
Depends on the Data Type. |
N/A |
No default |
Second input. |
|
IN2 |
ANY |
Depends on the Data Type. |
N/A |
No default |
Third input. |
|
IN3 |
ANY |
Depends on the Data Type. |
N/A |
No default |
Last input. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
ANY |
No range |
N/A |
IN0 or IN1 ... or IN3 depending on K. See the Truth Table. |
Remarks
None
Truth Table
|
K |
Q |
|---|---|
|
0 |
IN0 |
|
1 |
IN1 |
|
2 |
IN2 |
|
3 |
IN3 |
|
Other |
0 |
FBD Language Example
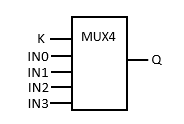
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD Language, the input rung (EN) enables the selection.
- The output rung keeps the state of the input rung.
- The selection is performed only if EN is TRUE.
- ENO has the same value as EN.
IL Language Example
- In the IL Language, the first parameter (selector) must be loaded in the current result before calling the function.
- Other inputs are operands of the function, separated by comas.
Op1: LD SELECT
MUX4 IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4
ST Q
ST Language Example
Q := MUX4 (K, IN0, IN1, IN2, IN3);
See Also






