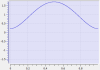
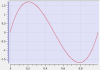
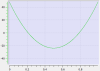
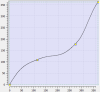
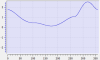
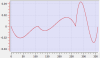
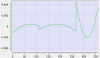
Cam Profile Segment Overview
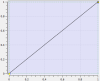
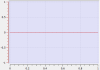
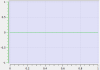
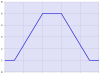
Line Segment Type
|
Segment Curve |
Velocity |
Acceleration |
Jerk |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Supported by |
KAS-IDE Profile Editor |
|
Continuous Velocity |
|
|
Continuous Acceleration |
|
|
Interpolation Method |
Linear function: f(x) = Ax + B |
|
Advantages |
This segment type easily defines constant-velocity segments. It can be used in very large numbers to define profiles of any size without having to specify the velocity or acceleration at the segment endpoints. |
|
Disadvantages |
Profiles can result in discontinuous velocities. |
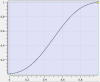
Parabolic Segment Type
|
Segment Curve |
Velocity |
Acceleration |
Jerk |
|---|---|---|---|
In the example:
- The blue line represents the linear (constant velocity) part of the segment.
- The black lines represent the parabolic (constant acceleration) parts of the segment.
|
Supported by |
KAS-IDE Profile Editor MLProfileBuild (parabolic option) |
|
Continuous Velocity |
|
|
Continuous Acceleration |
|
|
Interpolation Method |
Linear function: f(x) = Ax + B
|
|
Advantages |
This segment type is used to define constant acceleration portions of a profile. This minimizes the peak acceleration needed to move from one cam point to another. This can be useful when the motors cannot support the accelerations used by other segment types. |
|
Disadvantages |
Acceleration is discontinuous which can lead to additional electrical stress on the drives and motors. |
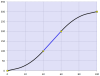
Point Segment Type
|
Segment Curve |
Velocity |
Acceleration |
Jerk |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Supported by |
KAS-IDE Profile Editor MLProfileBuild (default option) |
|
Continuous Velocity |
|
|
Continuous Acceleration |
|
|
Interpolation Method |
5th order polynomial: f(x) = Ax5 + Bx4 + Cx3 + Dx2 + Ex + F |
|
Advantages |
With only a few segments, this type can be used to define profiles with continuously changing accelerations. Example: Sinusoidal profiles can be emulated with 6 to 12 point segments. |
|
Disadvantages |
Specify the velocity and acceleration at the endpoints for each segment. It is difficult to use the point segment type to define constant acceleration or constant velocity segments. |
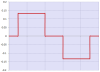
Spline Segment Type
|
Segment Curve |
Velocity |
Acceleration |
Jerk |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Supported by |
KAS-IDE Profile Import. The points are created by separate software and is imported into KAS-IDE project. |
|
Continuous Velocity |
|
|
Continuous Acceleration |
|
|
Interpolation Method |
3rd order polynomial: f(x) = Ax3 + Bx2 + Cx + D |
|
Advantages |
With only a few segments, this segment type can be used to define profiles with continuously changing velocities. Only the positions of the master and slave need to be specified. This produces smoother profiles than using line segments. |
|
Disadvantages |
Since only positions are specified, the user has less control over the velocities and accelerations that occur throughout the profile. |