Function Call
A 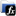 Function:
Function:
- Calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs.
- It has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances, unlike a function block.
- It has only one output: the result of the function.
- Examples of standard functions include AND, SHL, SIN, etc.
FBD Language and FFLD Language
To call a function in FBD or FFLD languages:
- Insert the function in the diagram.
- Connect its inputs and output.
IL Language
To call a function in the IL language:
- Load its first input parameter before the call.
- Use the function name as an instruction followed by the other input parameters, separated by comas.
The result of the function is then the current result.
This example demonstrates a call to ODD and SEL functions:
(* this statement converts any odd integer into "0" *)
Op1: LD iValue
ODD
SEL iValue, 0
ST iResult
ST Language
- Enter its name followed by the input parameters written between parentheses and separated by commas.
- The function call can be:
- inserted into any complex expression.
- used as an input parameter of another function.
This example demonstrates a call to ODD and SEL functions:
(* This statement converts any odd integer value into the nearest even integer: *)
iEvenVal := SEL ( ODD( iValue ), iValue, iValue+1 );
See Also






