S-curve and Trapezoidal Acceleration / Deceleration
S-curve
If the Jerk input of a motion function block is non-zero, S-curve acceleration / deceleration is used.
- The Acceleration input specifies the maximum acceleration reached when the velocity increases in magnitude.
- The Deceleration input specifies the maximum deceleration reached when the velocity decreases in magnitude.
- The Jerk input specifies the constant rate of change of acceleration and deceleration.
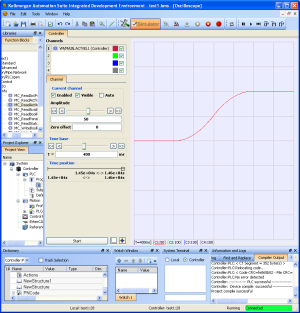
Small Jerk Acceleration
Figure 1 is a velocity plot of the acceleration of a move when Jerk is a small value.
The smaller the Jerk value, the more gradual the rate of change of acceleration and deceleration when transitioning from one velocity to another.
Figure 1: Small Jerk Acceleration
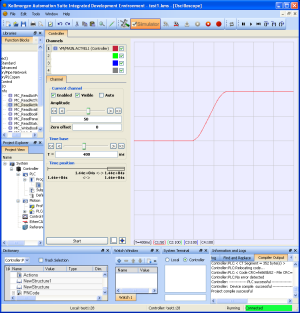
Large Jerk Acceleration
Figure 2 is a velocity plot of the acceleration of a move when Jerk is a large value.
The larger the Jerk value, the more abrupt the rate of change of acceleration and deceleration when transitioning from one velocity to another.
Figure 2: Large Jerk Acceleration
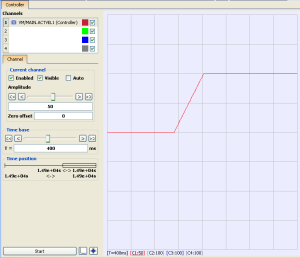
Trapezoidal
If the Jerk input of a motion function block is zero, trapezoidal acceleration and deceleration is used.
- The Acceleration input specifies the linear acceleration rate.
- The Deceleration input specifies the linear deceleration rate.
Figure 3 is a velocity plot of the acceleration of a move when trapezoidal acceleration is used (Jerk = 0 (zero)).