![]()
 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a master position
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a master position![]() Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different. phase shift
Position means a point in space which is described by different coordinates.
Depending on the used system and transformation it can consist of a maximum of six dimensions (coordinates).This means three Cartesian coordinates in space and coordinates for the orientation.
In ACS there can be even more than six coordinates.
If the same position is described in different coordinate systems the values of the coordinates are different. phase shift![]() Compensation for the lag between the electromagnetic and magnetic fields in the motor. for the slave axis.
Compensation for the lag between the electromagnetic and magnetic fields in the motor. for the slave axis.
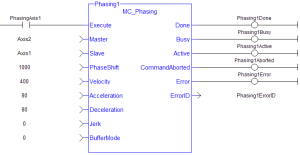
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Master |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function
|
|
Slave |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
AXIS_REF.AXIS_NUM is the slave axis number. See AXIS_REF Structure. |
|
PhaseShift |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Amount of phase shift. |
|
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec |
No default |
Velocity setpoint |
|
|
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Acceleration rate. S-curve: Maximum acceleration. |
|
|
Deceleration |
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Deceleration rate. S-curve: Unused. |
|
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec3 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: 0 (zero). S-curve: Constant jerk. |
|
|
BufferMode |
SINT |
0, 5 |
N/A |
No default |
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Done |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates the phase shift has been completely applied. |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
High from the moment the Execute input is one-shot to the time the move is ended. |
|
Active |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates this phase shift is the active phase shift. |
|
CommandAborted |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates the move was aborted. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates either:
|
|
ErrorID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates the error if Error output is TRUE. |
Remarks
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
- See Function Blocks - General Rules about how inputs and outputs work.
- See Main about how this function is used in the Hole punch project.
This function block:
- Provides a way to smoothly apply a master offset instead of writing values directly
 The orientation components of a vector in space. to the Master Offset Parameter 1002.
The orientation components of a vector in space. to the Master Offset Parameter 1002. - Is commonly used with MC_TouchProbe for performing position corrections on the slave axis in a Mark-to-Mark registration application.
-
- MC_Phasing performs a similar function to adjusting the MasterOffset input in the MC_CamIn function block.
It has the additional features of setting the velocity, acceleration, deceleration, and jerk motion parameters.
- The distance entered at the PhaseShift input is iterated into the Slave axis’s Master Offset.
- This distance is iterated like a MC_MoveRelative move using the specified Velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, and Jerk values.
- The difference is the interpolated command delta is not commanded to the axis but is added to the Slave axis’s Master Offset.
- This shifts the Master axis’s position as viewed by the Slave axis, causing a change in the Slave axis’s physical position.
- This only affects the Slave axis if it is executing a slave move.
- Subsequent calls to MC_Phasing can abort or blend to an executing MC_Phasing command.

Figure 1: MC_Phasing
FBD Language Example
Not available.
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
(* MC_Phasing ST example *) //Inst_MC_Phasing is an instance of MC_Phasing function block
Inst_MC_Phasing(PhasingAxis1, Axis2, Axis1, 1000.0,100.0, 200.0, 200.0, 0, 0 );