 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Enables
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Enables![]() Enable signal for the drive, Hardware-Enable with 24V signal to X8, Software-Enable command by setup Software, fieldbus or permanently set.
Both are required for enabling the drive. Mark-to-Machine registration.
Enable signal for the drive, Hardware-Enable with 24V signal to X8, Software-Enable command by setup Software, fieldbus or permanently set.
Both are required for enabling the drive. Mark-to-Machine registration.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
En |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Axis |
AXIS_REF |
The range of .AXIS_NUM is [1, 256] |
N/A |
N/A |
|
|
TriggerInput |
TRIGGER_REF |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
The structure elements are: Direction Range = 1, 5.
InputID INT Range = 0, 1
TrigIDINT Range = 0, 256.
|
|
Distance |
LREAL |
|
User units |
N/A |
|
|
Tolerance |
LREAL |
When converted to feedback units, |
User units |
N/A |
This value specifies the distance, plus or minus, about Distance to determine if the mark detected by the fast input is a good mark. |
|
Ignore |
LREAL |
|
User units |
N/A |
This value specifies the distance after the previous good mark in which any detected marks are ignored. |
|
Target |
LREAL |
When converted to feedback units,
|
User units |
N/A |
|
|
Position |
LREAL |
When converted to feedback units,
|
User units |
N/A |
|
|
PosAxis |
AXIS_REF |
The range of .AXIS_NUM is [1, 256] |
N/A |
N/A |
The position of this axis at the time the fast input occurs is compared to the Target position. This comparison determines the amount of registration compensation to apply. |
|
CompAxis |
AXIS_REF |
The range of .AXIS_NUM is [1, 256] |
N/A |
N/A |
The calculated registration compensation is applied to this axis. |
|
PosTolerance |
LREAL |
When converted to feedback units, the range is [-251, 251-1]. |
User units |
N/A |
This value specifies the distance, plus or minus, about the Target position to determine if the position is accepted and the compensation value is calculated and applied. |
|
RatioNumerator |
DINT |
When converted to feedback units, |
User units |
N/A |
|
|
RatioDenominator |
DINT |
When converted to feedback units, |
User units |
N/A |
|
|
Options |
UINT |
See the MC_MachRegist Options Table. |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
RegistOn |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates registration is activated. |
|
Aborted |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates registration has been terminated by MC_StopRegist. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates an invalid input was specified or the registration was terminated due to an error. |
|
ErrorID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
|
Remarks
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
-
- Is this the right function block to use?
See Decide which Function Blocks to Use for Registration and Registration Application Guide.
- It is used on any servo or digitizing axis and with any move type.
- It is used most frequently in master/slave applications.
|
Used with ... |
Effect |
|---|---|
|
Non-slave moves |
Resets |
|
Slave moves |
Applies a compensation offset to correct for the difference between the target position and the measured position. This provides the ability to compensate for product or process inconsistencies, provides a system that remains synchronized |
Transition and Registration
- A positive transition of the En input starts registration.
- The application may change the registration parameters while registration is active by changing the input values and causing another positive transition of the En input.
- The function block then reads and applies the new values.
- The axis number at the Axis input indicates the axis whose position, at the fast input, is used to determine if the mark is a good mark.
Distance, Tolerance, Ignore, Target Inputs
- The Distance, Tolerance, and Ignore inputs are used to determine whether or not the registration mark is good.
- For a mark to be recognized as good, it must be outside of the Ignore distance and the correct Distance from the previous mark +/- the Tolerance window.
- A mark is bad if it occurs outside of the “good tolerance band” and is not ignored.
- Both good marks and bad marks are recognized as marks, ignored marks are not recognized.
- If all marks are to be recognized as good marks, enter 0 (zero) at both Distance and Tolerance.
- The Distance value defines the distance between good marks.
- In Clear Lane and Product registration the Distance input value is typically the same as the Target input value.
- In Print registration, the Distance is typically not the same as Target.
- The Tolerance value is the distance, plus and minus, about Distance.
- Marks detected in this window are good marks and registration occurs.
- Marks detected outside this window and outside the Ignore band, are bad marks and registration does not occur.
- This window should be large enough to allow for the worst case error in the distance between the previous mark and the current mark.
- The Ignore value defines the distance from the previous mark where all marks detected by the fast input are ignored.
- This is crucial when registering products that do not have Clear Lane registration marks.
- The Target input is the expected target position that is used to calculate how much registration compensation is to be applied when a registration mark is considered good.
- When a good mark is detected, the position of the PosAxis is compared to the Target position to calculate a correction.
- The registration correction is only applied with master/slave move types.
Position and Option Inputs
- The Position input is the position value the registration Axis position is reset to when a good registration mark is detected.
- When a good mark occurs, the position of the PosAxis is compared to the Target position.
- This comparison is used to calculate the amount of registration compensation to apply to the CompAxis.
- Registration compensation is applied to the axis specified at the CompAxis input under these conditions:
- If CompAxis is a master axis, the compensation is applied to the master offsets of all its slaves.
- This shifts the master’s position as seen by its slaves.
- If CompAxis is executing a slave move (e.g., MC_GearIn or MC_CamIn), the compensation is applied directly to the axis.
- This comparison is used to calculate the amount of registration compensation to apply to the CompAxis.
- The PosTolerance input is the distance, plus and minus, about the Target position used to determine if compensation is applied.
- When a good mark occurs, the position of the PosAxis axis is checked to see if it lies in the window defined by PosTolerance.
- If it is in the window, compensation is applied.
- If it is outside the window, compensation is not applied even though a good mark was found.
- When a good mark occurs, the position of the PosAxis axis is checked to see if it lies in the window defined by PosTolerance.
- If PosAxis and CompAxis are different axes, the RatioNumerator and RatioDenominator inputs define the conversion factor for calculating the compensation value.
- This is needed because the amount of error between actual and target positions is determined by the PosAxis's position and the compensation is applied to the CompAxis.
- The RatioNumerator should typically be the number of User Units of CompAxis motion for one registration cycle.
- The RatioDenominator should typically be the number of User Units of PosAxis motion for one registration cycle.
- If PosAxis and CompAxis are the same, RatioNumerator and RatioDenominator should be the same value, thus resulting in a 1:1 ratio.
- When a good mark occurs, the position of the PosAxis is compared to the Target position.
- The Option input defines various modes of operation for registration.
- The first bit, 0001H, selects Absolute or Resetting.
- This refers to the way the second mark and all subsequent marks are determined to be good marks.
- With both registration schemes, the very first detected mark is the starting point.
- With Resetting registration, when the next mark is detected, the position of that mark becomes the starting point for the next good mark detection calculation and so on.
- The starting point is reset with each good or bad mark.
- This allows the product to re-synchronize, if necessary, due to process issues (e.g., product shift) etc.
- Absolute registration determines all good marks based on the very first mark.
- The position of the second and each subsequent mark is compared to an integer multiple of Distance from the very first mark.
- This method insures the product always registers to a known fixed distance.
- The starting point is reset with each good or bad mark.
- The third bit, 0004H, must be 0 (zero).
- Mark-to-machine registration requires time-based capture.
- The first bit, 0001H, selects Absolute or Resetting.
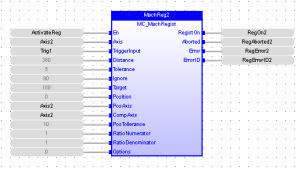
Figure 1: MC_MachRegist
MC_MachRegist Options Table
|
Hexadecimal |
Decimal |
Option |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
0001 H |
1 |
Absolute/Resetting |
0 = Resetting, 1 = Absolute |
|
0002 H |
2 |
Reserved |
0 |
|
0004 H |
4 |
Time/position based capture |
0 = time based capture, 1 = position based capture |
|
0008 H |
8 |
Inhibit Reference on Good Mark |
0 = Perform reference, 1 = inhibit reference When this bit is set, the Position function block argument is unused and the axis position is not changed when a registration mark is encountered. |
|
0010H |
16 |
Inhibit Master Compensation |
0 = Perform Master Compensation, 1 = Inhibit Master Compensation |
|
0020H |
32 |
Inhibit Slave Compensation |
0 = Perform Slave Compensation, 1 = Inhibit Slave Compensation. |
-
-
To use Capture Engine 1, modify the input PDOs that are used and add the Latch
 The control word is used to activate the drive's latch status machine.
The latch control word is processed independently of the EtherCAT® bus cycle.
The status word is used to return the drive's latch status. Position 1 parameter.
The control word is used to activate the drive's latch status machine.
The latch control word is processed independently of the EtherCAT® bus cycle.
The status word is used to return the drive's latch status. Position 1 parameter.
FBD Language Example
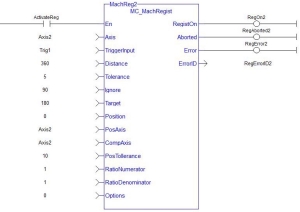
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
CAL Inst_MC_MachRegist( ActivateReg, Axist2, Trig1, 360, 5, 90, 180, 0, Axis2, Axis2, 5, 1, 1, 0 )
ST Language Example
Inst_MC_MachRegist( ActivateReg, Axist2, Trig1, 360, 5, 90, 180, 0, Axis2, Axis2, 10, 1, 1, 0 );
See Also