![]()
 Function
Function![]() A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Get a point from a Signal resource.
A function calculates a result according to the current value of its inputs. A function has no internal data and is not linked to declared instances. - Get a point from a Signal resource.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ID |
DINT |
|
|
|
ID of the signal resource, provided by the SigID function. |
|
TIME |
TIME |
|
|
|
Time (X) coordinate of the point within the signal resource. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
REAL |
|
|
Value (Y) coordinate of the point in the signal. |
Remarks
- The ID argument is the identifier of the signal resource.
- Use the SigID function to get this value.
- This function:
- Converts a time value to an analog value as defined in the signal resource.
- Can be used instead of the SigPlay function block to trigger the signal using a specific timer.
FBD Language Example
FFLD Language Example
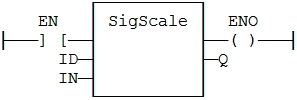
IL Language Example
Op1: LD"Ladder diagram" Ladder logic is a method of drawing electrical logic schematics. It is now a very popular graphical language for programming Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs). It was originally invented to describe logic made from relays. The name is based on the observation that programs in this language resemble ladders, with two vertical "rails" and a series of horizontal "rungs" between them IN
SigScale ID
ST Q
ST Language Example
Q := SigScale (ID, IN);
See Also







