![]()
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IN1 |
ANY |
|
|
|
First input. |
|
IN2 |
ANY |
|
|
|
Second input. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
BOOL |
|
|
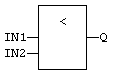
TRUE if IN1 < IN2. |
Remarks
- Both inputs must have the same type.
- Comparisons can be used with strings.
- With strings, the lexical order is used for comparing the input strings.
- Examples:
ABC is less than ZX.
ABCD is greater than ABC.
- Examples:
- With strings, the lexical order is used for comparing the input strings.
FBD Language Example
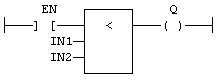
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.
- The output rung is the result of the comparison.
- The comparison is executed only if EN is TRUE.
IL Language Example
- In the IL Language, the LT
instruction performs the comparison between the current result and the operand.
- The current result and the operand must have the same type.
Op1: FFLD IN1
LT IN2
ST Q (* Q is true if IN1 < IN2 *)
ST Language Example
Q := IN1 < IN2;
See Also






