![]()
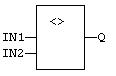
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
IN1 |
ANY |
|
|
|
First input. |
|
IN2 |
ANY |
|
|
|
Second input. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Q |
BOOL |
|
|
TRUE if IN1 is not equal to IN2. |
Remarks
- Both inputs must have the same type.
- Comparisons can be used with strings.
- With strings, the lexical order is used for comparing the input strings.
- Examples:
ABC is less than ZX.
ABCD is greater than ABC.
- Examples:
- With strings, the lexical order is used for comparing the input strings.
- Equality comparisons cannot be used with TIME variables.
- This is because the timer actually has the resolution of the target cycle and test can be unsafe as some values can never be reached.
FBD Language Example
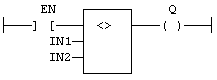
FFLD Language Example
- In the FFLD Language, the input rung (EN) enables the operation.
- The output rung is the result of the comparison.
- The comparison is executed only if EN is TRUE.
IL Language Example
- In the IL Language, the NE instruction performs the comparison between the current result and the operand.
- The current result and the operand must have the same type.
Op1: FFLD IN1
NE IN2
ST Q (* Q is true if IN1 is not equal to IN2 *)
ST Language Example
Q := IN1 <> IN2;
See Also