What MC_GrpHalt Does
MC_GrpHalt performs a controlled motion stop of all axes in a coordinated motion group.
See Differences between MC_GrpHalt and MC_GrpStop.
Example
This example demonstrates a linear coordinated move with a starting point of (0,0) and an endpoint of (200, 0).
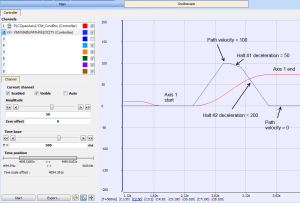
- The first and second MC_GrpHalt commands are called while the linear coordinated move is still moving to the endpoint.
- In the oscilloscope, the second call to MC_GrpHalt aborts the first MC_GrpHalt as seen by the new deceleration rate.
- The path velocity reaches zero (approximately (60, 0)) before the linear coordinated move reaches its endpoint value.
-
-
For demonstration purposes, it is assumed that the axes and group have been properly setup and configured.
Example steps to setup coordinated motion are listed in Create a Linear or Circular Coordinated Motion Application.
1: // Perform Linear ABSOLUTE move start (0,0) end (200,0)
PosAbs[0]:= 0;
PosAbs[1]:= 200;
PosAbs[2]:= 0;
pathVelocity := Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel2.PathVelocity;
Inst_MC_MoveLinAbs(TRUE, Group1_ref, PosAbs, Velocity, Acceleration, Deceleration, Jerk, CS_ACS, BM_ABORTING, TM_NONE, TransParam);
Inst_TON3(true, t#600ms); //Allow for the move to reach path velocity before calling MC_GrpStop
Inst_TON3.Q THEN
MC_MoveCounter := MC_MoveCounter + 1;
Inst_TON3(false, t#100ms);
END_IF;
2: //Perform a halt on the group
halt_deceleration := 50.0;
pathVelocity := Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel2.PathVelocity;
Inst_MC_GrpHalt(TRUE, Group1_ref, halt_deceleration, default_jerk);
Inst_TON3(true, t#200ms); //Allow for first halt deceleration rate to be captured on the scope
IF Inst_TON3.Q THEN
MC_MoveCounter := MC_MoveCounter + 1;
Inst_TON3(false, t#100ms);
END_IF;
3: // Perform a second halt increasing the deceleration value.
// The second call to MC_GrpHalt will abort the first MC_GrpHalt
halt_deceleration := 200.0;
pathVelocity := Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel2.PathVelocity;
Inst_MC_GrpHalt1(TRUE, Group1_ref, halt_deceleration, default_jerk);
Inst_TON3(true, t#200ms);
IF ((Inst_TON3.Q) and (Inst_MC_GrpHalt1.Done Or Inst_MC_GrpHalt1.Error)) THEN
Inst_TON3(false, t#100ms);
Inst_MC_MoveLinAbs(FALSE, Group1_ref, PosAbs, default_velocity, default_acceleration, default_deceleration, default_jerk,
CS_ACS, BM_ABORTING, TM_NONE, TransParam);
Inst_MC_GrpHalt1(FALSE, Group1_ref, default_deceleration, default_jerk);
END_IF;
When MC_GrpHalt is called in the example:
- The current move is aborted.
- A controlled motion stop is applied to axes group Group1_ref.
- The deceleration value, halt _deceleration is set to 50.0 User unit/sec2 on the first call and 200.0 User unit/sec2 on the second call.
- It is applied to the path velocity until it reaches 0 (zero) when the MC_GrpHalt command is issued during a coordinated motion move.
- The group state is GroupMoving while the coordinated move is decelerating.
- The group state goes to GroupStandBy once the path velocity reaches 0 (zero).
- Any coordinated moves in the buffer are flushed.
- New coordinated moves can be queued up upon completion of the MC_GrpHalt command.
-
-
This behavior is different than the ccpMC_GrpStop command.
See Differences between MC_GrpHalt and MC_GrpStop.
Figure 1: Oscilloscope Representation of linear coordinated move with a MC_GrpHalt command called twice.
Exceptions
- The deceleration rate from the MC_GrpHalt function block is only applied to the absolute and relative coordinated motion moves.
- Direct coordinated motion moves use the default deceleration value as defined by the AxisRef.
- MC_GrpHalt cannot occur if a group is not enabled.
- An MC_GrpHalt command may be aborted by another MC_GrpHalt command, a ccpMC_GrpStop command or a MC_Move* command.
- When there are two coordinated motion moves (Active and Next) in the queue, and the path velocity does not reach 0 (zero) before the end of the Active move, the path velocity continues to reach zero during the Next move.
- The deceleration rate is increased if there is only one Active coordinated move and the path velocity cannot reach zero before the endpoint.
- This prevents overshooting the endpoint.
- The halt action pauses during S-Curve Corner transitions.
- Any halt in progress continues after the S-Curve Corner transition is complete.
- If a halt is started during an S-Curve Corner transition, the halt action starts after the S-Curve Corner transition completes.
- While a halt action is in progress, there may be a discontinuity in acceleration at the endpoints of S-Curve Corner transition.
- An MC_GrpHalt command does not prevent performing a single axis motion.