![]()
![]()
 Function Block
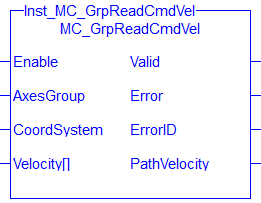
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Reads the command velocity of the axes in the group and the path velocity.
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Reads the command velocity of the axes in the group and the path velocity.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Enable |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
If TRUE, this function block reads the current commanded velocity of the group and the axes in the group. |
|
AxesGroup |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
The axes group the commanded velocity is read from. |
|
|
CoordSystem |
SINT |
One of these enumeration values:
|
N/A |
No default |
The coordinate system used when reading the commanded velocity. |
|
Velocity[ ] |
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec |
No default |
An array where the velocity data is written.
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Valid |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
If TRUE, the velocities were read without error. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
If TRUE, an error has occurred. |
|
ErrorID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates the error if Error output is TRUE. See the table in PLCopen Function Block ErrorIDs. |
|
PathVelocity |
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec |
The current commanded path velocity of the group. This is measured by taking the square root of the sum of the squared velocities of each axis. |
Remarks
-
-
This function or function block returns cached data.
See Program a Multi-Core Controller for more information.
- See Coordinated Motion, the top-level topic for Coordinated Motion.
- See Function Blocks - General Rules for more information about how inputs and outputs work.
- The MC_GrpReadCmdVel function block fills the array specified by the
Velocityargument with the commanded velocity for the coordinate system, which is specified by theCoordSystemargument.- The path velocity is reported by the PathVelocity output.
- This function or function block does not generate any motion.
-
-
Currently, only the ACS coordinate system is supported.
See Coordinate Systems for more information.
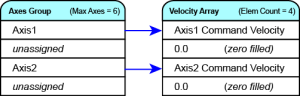
- There is a one-to-one correspondence between the axes in the Axes Group and the velocity values in the Velocity Array.
- Each element in the Velocity Array corresponds to the axis element in the Axis Group array.
- If a index in the Axes Group is unassigned, the velocity value for that array element in the Velocity array is 0 (zero).
- If a index in the Axes Group is unassigned, the velocity value for that array element in the Velocity array is 0 (zero).
- If the element does contain an axis, the velocity value is filled with the current velocity for that axis.
Figure 6-143: MC_GrpReadCmdVel
FBD Language Example
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
BEGIN_IL "Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly
"Instruction List"
This is a low-level language and resembles assembly
CAL Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel( DoRead, Group, CoordSys, VelList )
END_IL
ST Language Example
(*MC_GrpReadCmdVel ST "Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal example *)
Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel(DoRead, Group, CoordSys, VelList );
"Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal example *)
Inst_MC_GrpReadCmdVel(DoRead, Group, CoordSys, VelList );
See Also