![]()
 Function Block
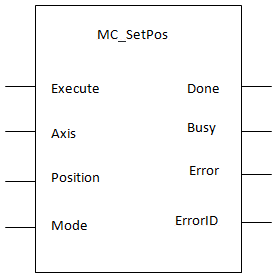
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Changes the present actual position of the axis (as reported by MC_ReadActPos) to the position specified by the Position and Mode inputs.
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Changes the present actual position of the axis (as reported by MC_ReadActPos) to the position specified by the Position and Mode inputs.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Axis |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function.
|
|
Position |
LREAL |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
Absolute Mode: New Axis Position to replace the present position. Relative Mode: Position offset to apply to present position. Typically used with multi-turn absolute position feedback devices. |
|
Mode |
BOOL |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
LOW = Position input is an absolute position. HIGH = Position input is a relative position |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Done |
BOOL |
|
|
Indicates the reference move and position adjustment is complete. |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
|
|
Indicates this function block is executing. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
|
|
Indicates either:
|
|
ErrorID |
INT |
|
|
Indicates the error if Error output is high. See PLCopen Function Block ErrorIDs for more information. |
Remarks
-
-
This function or function block returns cached data.
See Program a Multi-Core Controller for more information.
- See Function Blocks - General Rules for more information about how inputs and outputs work.
- If a motor is associated with the axis, it does not move when MC_SetPos is executed.
- MC_SetPos does not cause any motion.
- It applies an offset to the command and actual positions.
- MC_SetPos sets the accumulated Superimposed distance value for the input axis to 0 (zero).
- See Axis Positions Data for more information.
- This function block replaces MC_SetPosition.
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
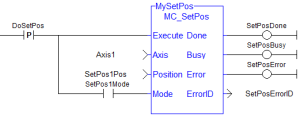
Figure 6-257: MC_SetPos
FBD Language Example
Not available.
FFLD Language Example
-
- This function block finishes immediately.
Because of this, the Done output does not get set to FALSE in a second call to the same MC_SetPos instance unless there is an error.
If the application needs to look for a state change to determine if a particular call to MC_SetPos was successful, then useANDfor the rising edge of the Execute input, the Done output, and the inverse of the Error output.
This FFLD "Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language example shows how this can be done.
"Free Form Ladder Diagram" Language example shows how this can be done.
In the example, the SetPosSuccessful variable is set toTRUEfor one cycle upon a successful call to the MC_SetPos instance.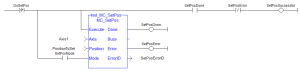
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
(* MC_SetPos ST "Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal example *)
"Structured text"
A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal example *)
Inst_MC_SetPos ( Axis1 , 0, 0 );
//Inst_MC_SetPos is an instance of MC_SetPos function
(* MC_SetPos absolute mode example: Set position value to zero. *)
Inst_MC_SetPos ( Axis1 , 0, 0 );
//Inst_MC_SetPos is an instance of MC_SetPos function
(* MC_SetPos relative mode example: Increase position value by 1000. *)
Inst_MC_SetPos ( Axis1 , 1000, 1 );
//Inst_MC_SetPos is an instance of MC_SetPos function