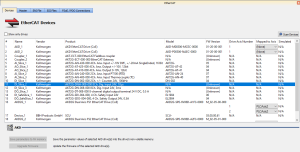
EtherCAT Devices tab
The EtherCAT![]() ***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs Devices tab lists all the EtherCAT devices and provides for the ability to discover and map their use.
***EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs Devices tab lists all the EtherCAT devices and provides for the ability to discover and map their use.
- The interface is slightly different for AKD and AKD2G drives.
- The AKD2G prompts you to select the mapping by the drive axis.
Figure 4-101: EtherCAT Devices Summary Form
First generation AKD drives support one axis per drive, while AKD2G drives support two axes per drive.
When configuring drives in the EtherCAT Devices tab, you need to designate which motion axis applies to each drive axis, which is the actual axis the drive controls.
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Show only drives |
This option hides all |
| Scan Devices |
The KAS Runtime See Scan Devices. |
| Name, Vendor, Product, and Model |
|
| FW Version |
|
| Drive Axis Number |
|
| Mapped to Axis |
For each drive, it is displayed if it is:
|
| Simulated |
Used to simulate the device, which means that the device is not used and no communication to this device is performed through the fieldbus. |
| Save parameters to NV memory |
|
| Upgrade Firmware |
|
Scan Devices
The scan process allows these tasks:
- Discover the devices and modules physically present in the fieldbus network.
- Map them to items under the EtherCAT node of the Project Explorer
- The order of the devices in the tree is the same as in the real fieldbus network.
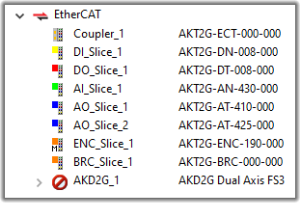
Figure 4-102: EtherCAT Network - Physical View
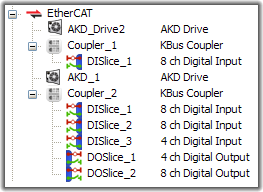
K-Bus |
E-Bus |
During the scan operation, all physical devices connected to the EtherCAT network are discovered and identified.
- The KAS-IDE lists the devices in the order they are connected.
- Kollmorgen devices, which include AKD and S300
 "Servostar 300 drive"
See Servo Drive in Glossary/S700
"Servostar 300 drive"
See Servo Drive in Glossary/S700 "Servostar 700 drive"
See Servo Drive in Glossary drives, Standard I/O Couplers, and remote I/O terminals, include detailed information for each device.
"Servostar 700 drive"
See Servo Drive in Glossary drives, Standard I/O Couplers, and remote I/O terminals, include detailed information for each device. - See Remote Input/Output Terminals for a list.
The status of devices can be determined by their icon in the logical view.
| Icon | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
| (device icon) | Normal |
The device has been added by scanning the system. The associated ESI file has been found. The icon varies by device, but is the icon set by the manufacturer in the ESI file. |
|
|
Excluded |
The device has been added manually or has been disassociated from a discovered device. |
|
|
ESI missing |
The ESI file is missing. |
|
|
Error |
For AKD, shown when there is an error. |
Scan Limitations
- I/O slices for Standard I/O Coupler do not reveal their Device IDs.
- The discovery feature does not differentiate between AKT-DN-004-000 and AKT-DNH-004-000 I/O terminals.
- Nor between AKT-DN-008-000 and AKT-DNH-008-000.
- Devices other than those made by Kollmorgen are identified by the Vendor Name (or ID number) and Product Name (or ID number).
- ESI files for any MDP devices connected to the network should be added to KAS-IDE's ESI library before starting a scan.
- If the ESI file for an MDP device is not available, then the scan cannot identify the device and cannot discover any physical or logical modules under the device.