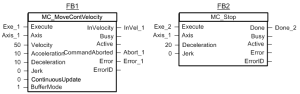
MC_MoveContVel
![]()
 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a single-axis non-ending move at a specified velocity
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data.
It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a single-axis non-ending move at a specified velocity![]() For a group of axes this means: In ACS the velocities of the different axes. In MCS and PCS it provides the velocity of the TCP with the option of continually updating the ongoing motion with the current input parameters.
For a group of axes this means: In ACS the velocities of the different axes. In MCS and PCS it provides the velocity of the TCP with the option of continually updating the ongoing motion with the current input parameters.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Axis |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function
|
|
Velocity |
LREAL |
All finite values. |
User unit/sec |
No default |
The target axis velocity.
|
|
LREAL |
Positive values. |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Acceleration rate. S-curve: Maximum acceleration. |
|
|
Deceleration |
LREAL |
Positive values. |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Deceleration rate. S-curve: Unused. |
|
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec3 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: 0 (zero). S-curve: Constant jerk. |
|
|
ContinuousUpdate |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
No default |
Determines if the inputs of the function block are re-evaluated every cycle or if they are only evaluated on the rising edge of Execute.
|
|
BufferMode |
SINT |
See Description |
N/A |
No default |
The specified buffer mode.
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
InVelocity |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
Indicates the command velocity has reached the programmed |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
High from the moment the Execute input goes high until the time the move is ended. |
|
Active |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
Indicates this move is the Active move. |
|
CommandAborted |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
Indicates the move was aborted. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
Indicates either:
|
|
ErrorID |
INT |
-32768 to +32767 |
N/A |
Indicates the error if Error output is TRUE. |
Remarks
-
-
This function or function block returns cached data.
See Program a Multi-Core Controller.
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
- After MC_MoveContVel execution begins (Execute input - low to high), follow up changes to input parameters immediately affect the ongoing motion, without requiring an additional low to high transition on the Execute input.
- This type of move can be terminated with the MC_Halt function block or by aborting it with another move.
Figure 1: MC_MoveContVel
Time Diagram
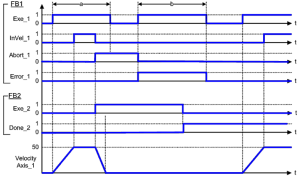
This example shows the behavior of the combination of a MC_Stop function block with a MC_MoveContVel function block.
- A rotating axis is ramped
 The gradual acceleration and deceleration of a stepping motor.
This is essential if performance beyond the start/stop range is required.
The slope of the ramp is a function of screw pitch, load, drive voltage and design, and motor. down with FB2 MC_Stop.
The gradual acceleration and deceleration of a stepping motor.
This is essential if performance beyond the start/stop range is required.
The slope of the ramp is a function of screw pitch, load, drive voltage and design, and motor. down with FB2 MC_Stop. - The axis rejects motion commands as long as MC_Stop parameter Execute = TRUE.
- FB1 MC_MoveContVel reports an error indicating the busy MC_Stop command.
Figure 2: Time Diagrams: First and Second FBs
Figure 3: Time Diagram
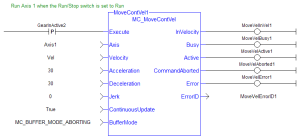
FBD Language Example
Not available.
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
(* MC_MoveContVel STStructured text - A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal. example *)
Inst_MC_MoveContVel( MovVelReq , Axis1, Vel, 100.0, 100.0, 0, True, MC_BUFFER_MODE_ABORTING );
See Also