Programs: Structure and Syntax
This section provides details on the syntax, structure, and use of the declarations and statements supported by the KAS IDE![]() "Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger application language.
"Integrated development environment"
An integrated development environment is a type of computer software that assists computer programmers in developing software.
IDEs normally consist of a source code editor, a compiler and/or interpreter, build-automation tools, and a debugger application language.
Project Structure
Structuring the application with care is important in creating your project.
See Project Structure Guidelines in the Advanced Topics.
IEC 61131-3 Editors
The KAS IDE programming environment provides
- Free Form Ladder Diagram (FFLD) Editor
- Function Block Diagram (FBD) Editor
- Sequential Function Chart (SFC) Editor
- Structured Text (ST) / Instruction List (IL) Editor
A more extensive description on each language can be found in these sections of the Technical References:
- SFC must be used when you need to manage sequences of stable process states.
- Using SFC avoids complex switches and the declaration of multiple flags in programs.
- SFC must never be used as a decision diagram or flow chart for describing an algorithm (e.g., when you think “If / Then / Else...”).
- This leads to complex SFC charts and bad performances at run-time
 In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running.
In computer science, runtime (or run-time) describes the operation of a computer program, the duration of its execution, from beginning to termination (compare compile time).
Within KAS, runtime also refers to the virtual machine that manage the program written in a computer language while it is running.
- This leads to complex SFC charts and bad performances at run-time
- Never use a step to represent an intermediate point within a calculation.
- Use ST in this case.
See also Program Limitations and the PLC Online Change feature.
Tips
Drag-and-Drop
The editor provides you with an ideal programming environment, including drag-and-drop features:
- Drag a variable from Dictionary and drop it into the program to insert it
- Drag a definition from Libraries and drop it into the program to insert its name
- Drag a block and drop it into the program to insert it (you can even select the block from an external text file).
- Drag a function block to the variable list to declare an instance
Auto-completion
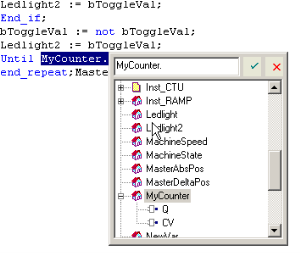
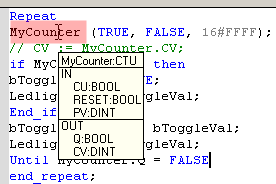
When you type the name of a function block instance (e.g., use either as an instance or a data structure), press the point (.) after the name of the instance opens a pop-up list with the names of possible elements.
Click the relevant element and validate it with the check mark.
Figure 4-70: Autocompletion
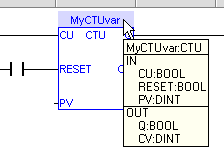
Tooltip on Variable
When you leave the mouse cursor on a variable in Editors, a tooltip is shown to give you more details on the item.
Figure 4-71: Tooltip on Variable
The header of the tooltip shows the name of the variable and its type.
Bookmarks
See Bookmarks
Select Function Blocks
All available Operators, functions and function blocks are listed in the Libraries toolbox.
- The list of available blocks is sorted into categories.
- The (All) category is used to see the complete list of available blocks.
Insert a Block in a Program
Select a block and drag-and-drop it to its position in the Editor.
-
-
Drag a function block from the Libraries and drop it in the variable list (Dictionary) to declare a new instance.
Then drag this instance from the Dictionary and drop it in the program.
Select Variables and Instances
Symbols of variables and instances are selected using the variable list in the Dictionary.
Selecting variables is available from all editors:
- In FBD diagrams, double-click on a variable box, an FB instance name, a contact or a coil to select the associated variable.
- In FFLD diagrams, double-click on a contact, a coil or a block input or output to select the variable.
Double-click on the top of an FB rectangle to select an instance.
- When the variable editor is visible in the editor window, you can drag a variable from the list and drop it in the program to insert it.
Access a Single Bit of an Integer Variable
<variable>.<Bit number> (e.g., MachineState.7)