 Function - Performs a move to an absolute position.
Function - Performs a move to an absolute position.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ID |
DINT |
-2147483648 to 2147483647 |
N/A |
No default |
ID Name of the Axis block. |
|
Position |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Sets the value of the absolute destination position. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Default (.Q) |
BOOL |
FALSE, TRUE |
N/A |
Returns TRUE when the function successfully executes. See Function - General Rules. |
Remarks
- This function sets a new target Generator Position.
- Returns TRUE if the function succeeded.
- See Axis Function Examples.
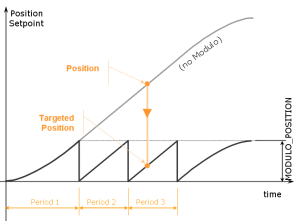
Position with Modulo On
-
- This information applies to both MLAxisAbs and MLMstAbs.
For simplicity, the term Axis Block also refers to Master Block.
When the Modulo is turned on, the Axis Block moves to the targeted position during the corresponding period and is calculated as:
- If the Position input is between 0 (zero) and the Modulo position, the Axis Block moves within the current period (no position rollover).
- If the Position input is greater than the Modulo position, the Axis Block moves during one of the next period (positive position rollover).
Figure 1: MLAxisAbs or MLMstAbs Modulo
The Axis Block works similarly for negative positions.
If the Position input is less than 0 (zero), the Axis Block moves during one of the previous period (negative position rollover).
Forcing the Direction of Rotation
In some applications, the direction of rotation for the axis is forced in one direction only.
As a consequence, the motor movement goes to the next or previous modulo in these situations:
End Position is Less Than Start Position
If the End Position is less than the Start Position and the direction of rotation for the axis is forced to be clockwise, the red point shows when the Modulo position is reached.
See Row 2 of the MLAxisAbs.
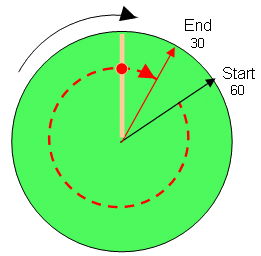
Figure 2: MLAxisAbs or MLMstAbs - End Position Less Than Start Position
End Position is Greater Than Start Position
If the End Position is greater than the Start Position and the direction of rotation for the axis is forced to be counter clockwise.
See Row 4 of the MLAxisAbs.
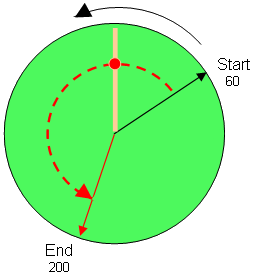
Figure 3: MLAxisAbs or MLMstAbs - End Position Greater Than Start Position
|
Start Position |
End Position |
Direction of Rotation |
Cross Modulo |
Position Input to MLAxisAbs (1) |
RelativeDistance Moved (2) |
|
|
60 |
200 |
Clockwise |
No |
200 |
140 |
(i.e., 200 - 60 + 0) |
|
60 |
30 |
Clockwise |
Yes |
390 |
330 |
(i.e., 30 - 60 + 360) |
|
60 |
30 |
Counter clockwise |
No |
30 |
-30 |
(i.e., 30 - 60 - 0) |
|
60 |
200 |
Counter clockwise |
Yes |
-160 |
-220 |
(i.e., 200 - 60 - 360) |
With:
(1) Position Input = End Position ( + Modulo * Direction of rotation)
(2) Relative Distance Moved = End Position - Start Position ( + Modulo * Direction of rotation)
Where:
Direction of rotation = 1 when clockwise and -1 when anti-clockwise.
Travel Speed Update with MLAxisAbs
The travel speed of the generator can be updated using the function block MLAxisGenWriteSpd.
Depending on the state of the generator, this speed is directly reflected on the current move or a future move.
- If MLAxisAbs is not currently being executed, the new travel speed is applied for the trajectory calculation for a future MLAxisAbs command.
- If MLAxisAbs is currently being executed, and a new MLAxisAbs with the same target position is called, the new travel speed is taken into account only if the current state of the TMP profile is the constant velocity or acceleration.
- If the axis was decelerating to stop at the goal position the new travel speed is not taken into account.
- If a MLAxisAbs is currently being executed, and a new MLAxisAbs with a different target position is called, the new travel speed is taken into account.
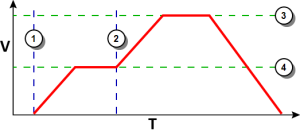
Example 1
|
Figure 4: Initial speed is smaller than the new speed.
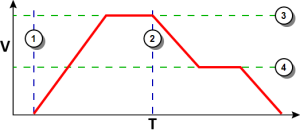
Example 2
|
Figure 5: Initial speed is bigger than the new speed.
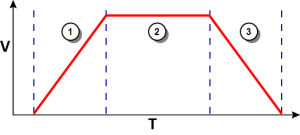
Example 3
|
Figure 6: The speed update is taken into account only if the second MLAxisAbs is triggered during acceleration or constant velocity.
FBD Language Example
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
MLAxisAbs( PipeNetwork.Axis1, 2000 ) ;
See Also