PLCopen Registration
Registration is a technique used to maintain the positional accuracy in repetitive processes.
- It uses a Fast Input switch, typically a photo eye, to measure product position and adjust the axis (or axes) to compensate for variations.
- The basic forms of registration are:
Decide which Function Blocks to Use for Registration
These are the methods to set up Registration, each using a different set of function blocks.
Method 1 is easy to set up, thus we recommend trying it first.
|
|
Method 1: Using MC_TouchProbe |
Method 2: Using MC_MarkRegist or MC_MachRegist |
|---|---|---|
|
Key Function Blocks |
|
|
|
Details |
This method incorporates:
|
This method incorporates:
|
|
Advantages |
Basic implementation.
|
Incorporates additional functionality including:
|
|
Example |
Master/Slave Registration
Master/slave registration is performed on an axis running a master/slave move (e.g., MC_CamIn or MC_GearIn).
- It can be performed by tracking the position of the master axis (Master Registration) or tracking the position of the slave axis (Slave Registration) or both.
- This type of registration:
- Adjusts the positional relationship between the master and slave axes to accommodate for variations in the distance between products.
- Keeps the process synchronized to the product over many repetitions.
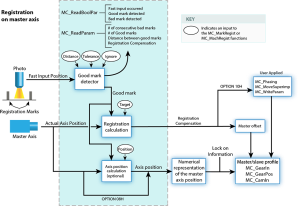
Master Registration
Master registration is performed by having the Fast Input switch trigger on a registration mark controlled by the master axis.
- When the Fast Input latches the position of the master axis at this mark, the distance between this position and the position of the previous mark is compared to an expected distance.
- This difference is added to the slave axis's master offset to adjust the position of the slave axis with respect to the position of the master.
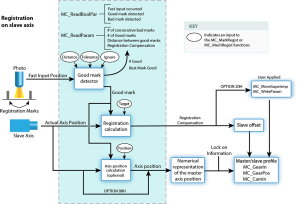
Slave Registration
Slave registration is performed by having the Fast Input switch trigger on a registration mark controlled by the slave axis.
- When the Fast Input latches the position of the slave axis at this mark, the distance between this position and the position of the previous mark is compared to an expected distance.
- This difference is added to the slave axis's slave offset to adjust the position of the slave axis with respect to the position of the master.
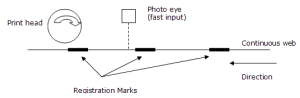
This Registration image is an example of a printing application using registration.
- The axis controlling the web is the master and the axis controlling the print head is the slave.
- When the photo eye detects a registration mark on the web, the master position is latched.
- The amount of registration compensation required is calculated by comparing the actual distance between the marks to the expected distance.
- That difference is added to the slave axis’s master offset.
- This adjusts the positional relationship between the web and the print head so that each print on the web is placed accurately.
Single-Axis Registration
Single-axis registration is performed on an axis running a discrete move such as MC_MoveAbsolute or MC_MoveRelative.
- When the Fast Input latches the position of the product, the axis position is reset, typically to 0 (zero).
- This resets the axis's coordinates for each product to accommodate for variations in the distance between products and keep the process synchronized to the product over many repetitions.