![]()
 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a slave axis move which follows the master axis based on the Cam Table specified by CamTableID.
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Performs a slave axis move which follows the master axis based on the Cam Table specified by CamTableID.
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Master |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function.
|
|
Slave |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
AXIS_REF.AXIS_NUM is the slave axis number. See AXIS_REF Structure for more information. |
|
MasterOffset |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Master axis offset. This input is not used if the StartMode input is set to 1 for Resume Mode. |
|
SlaveOffset |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Slave axis offset. This input is not used if the StartMode input is set to 1 for Resume Mode. |
|
MasterScaling |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Master axis scale factor.
|
|
SlaveScaling |
LREAL |
No range |
User units |
No default |
Slave axis scale factor.
|
|
StartMode |
INT |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
Starting mode of the cam profile. The function block uses values that were in effect during the most recently programmed MC_CamIn move for the slave axis. 0 = Start Mode
1 = Resume Mode
|
|
CamTableID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
No default |
Profile ID number. |
|
BufferMode |
SINT |
N/A |
No default |
The Buffer mode for CamIn block.
|
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
InSync |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates the slave axis is in sync with the profile. |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates this function block is executing. |
|
Active |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates this move is the Active move. |
|
CommandAborted |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates the move was aborted. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates either:
|
|
ErrorID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
Indicates the error if the Error output is high. See PLCopen Function Block ErrorIDs for more information. |
|
EndOfProfile |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates the end of profile has been reached.
|
Remarks
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
- This function block is used to either:
- Initiate a new MC_CamIn move.
- Resume a previously programmed MC_CamIn move.
- See MC_CamStartPos or MC_CamResumePos for more information about positioning the slave axis prior to calling MC_CamIn.
- See Function Blocks - General Rules for more information about how inputs and outputs work.
Abort Camming
-
-
Ending camming is also possible with other single axis function blocks (e.g., MC_MoveRelative or MC_MoveAbsolute).
There are two options to stop camming after MC_CamIn has been called:
- MC_CamOut continues motion at the instantaneous final actual velocity of the slave axis when it is called.
- Axis motion continues at that final actual velocity.
- MC_Halt (with buffer mode input = 0) decelerates axis motion to 0 (zero) speed and stop motion.
- The master / slave relationship between the two axes is ended when MC_CamOut or MC_Halt is called.
Figure 6-244: MC_CamIn
Usage
The slave axis immediately locks on to the Cam Table profile.
- The Master Offset is used to shift the profile along the master axis.
- The Master Scaling defines the range of the profile along the master axis.
- The Slave Offset is used to shift the profile along the Slave axis.
- The Slave Scaling defines the range of the profile along the slave axis.
Periodic or Not Periodic
- If the profile is periodic, when the end of profile is reached, the profile continues at the start of the profile.
- The EndOfProfile output is ON for 1 ladder scan.
- If the profile is not periodic, when the end of profile is reached, the slave axis stops and remains at the end of the profile until the master axis returns to within the profile range as defined by MasterScaling.
- The EndOfProfile output remains ON anytime the master axis is outside of the profile range.
Adjustments Computation is Done
When cam is first started, offsets are adjusted if necessary.
- If the master is not absolute, then master offset = master offset + starting position.
- If the slave is not absolute, then slave offset = slave offset + starting position.
- Master position for profile = master position - master offset.
- Use master position for profile table to obtain slave profile position.
- Slave commanded position = slave profile position + slave offset.
Dynamically Change a Cam Profile
MC_CamIn can be used to dynamically change from one cam profile to another.
Care must be taken when doing this to avoid unexpected motion.
-
-
Tips to dynamically change cam profiles:
- Verify the first cam’s last position and the replacement cam’s first position are the same.
- Offsets as set byMC_CamTblSelect affect actual cam position.
- Verify the first cam’s last velocity and the replacement cam’s first velocity do not cause any unexpected motion.
- Jumps can be eliminated by defining the present cam as Cyclic and defining the replacement cam as an Absolute Master and Slave, as set by the MC_CamTblSelect inputs.
- This eliminates any possible small error accumulating when the cam is switched.
- Verify the first cam’s last position and the replacement cam’s first position are the same.
Examples
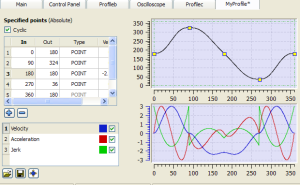
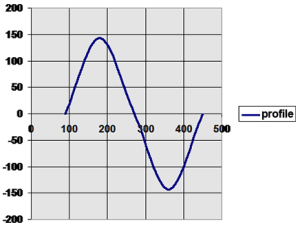
These examples use the MC_CamIn Example image showing the cam profile MyProfile:
Figure 6-245: MC_CamIn Example
Example 1
|
Profile |
MyProfile |
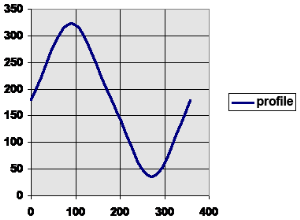
|
|
Cycle |
NO |
|
|
MasterAbsolute |
YES |
|
|
SlaveAbsolute |
YES |
|
|
MasterOffset |
0.0 |
|
|
SlaveOffset |
0.0 |
|
|
MasterScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
SlaveScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
Initial Master position |
0.0 |
|
|
Initial Slave position |
180.0 |
After MC_CamTblSelect and MC_CamIn are programmed with the parameters, the slave axis is locked on to the profile.
- Since both axes have zero offsets, the profile is not shifted in either axis.
- The initial condition of the master axis at position 0 (zero), yields a slave command position of 180.0.
- As the master axis moves positive, the slave position follows the profile.
- When the master position is at 90.0, the slave is commanded to 324.0.
- See curve below where in = 90, out = 324.
- The slave follows the profile as the master axis moves until the master axis reaches a position of 360.0.
- At this time, the slave is commanded to 180.0.
- If the master were to continue to move past 360.0, the slave commanded position would remain at 180.0 since the Cyclic input is false.
- If the master moves negative, and its position returns to less than 360.0, the slave follows the profile again.
Example 2
|
Profile |
MyProfile |
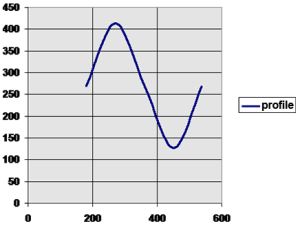
|
|
Cycle |
YES |
|
|
MasterAbsolute |
NO |
|
|
SlaveAbsolute |
NO |
|
|
MasterOffset |
0.0 |
|
|
SlaveOffset |
0.0 |
|
|
MasterScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
SlaveScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
Initial Master position |
180.0 |
|
|
Initial Slave position |
90.0 |
After MC_CamTblSelect and MC_CamIn are programmed with the parameters, the slave axis is locked on to the profile.
- Since both axes have zero offsets, the profile is not shifted in either axis.
- Neither the MasterAbsolute nor SlaveAbsolute input is on, so the profile is relative to the axes initial positions.
- Specifically, the initial condition of the master axis at position 180 would represent a master profile position of 0 (180-180).
- This yields a slave command position of 270 (180 + 90).
- As the master axis moves positive, the slave position follows the profile.
- When the master position is at 270, the slave is commanded to 414.0 (324 + 90).
- The slave follows the profile as the master axis moves until the master axis reaches a position of 540.
- At this time the slave is commanded to 270.0 (180 + 90).
- If the master continues to move past 540.0, the slave commanded position follows the profile from the beginning since the Cyclic input is TRUE.
- When the master reaches a position of 630, the slave is commanded to a position of 414.0 (324 + 90).
Example 3
|
Profile |
MyProfile |
|
|
Cycle |
NO |
|
|
MasterAbsolute |
YES |
|
|
SlaveAbsolute |
YES |
|
|
MasterOffset |
90.0 |
|
|
SlaveOffset |
-180 |
|
|
MasterScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
SlaveScaling |
360.0 |
|
|
Initial Master position |
180.0 |
|
|
Initial Slave position |
144.0 |
After MC_CamTblSelect and MC_CamIn are programmed with the parameters, the slave axis is locked on to the profile.
- Since the both axes have offsets, the profile is shifted along both axes.
- Specifically, the master axis is shifted 90, and the slave axis is shifted -180.
- Initially the master axis position of 180 yields a master position for the profile calculation of 90 (master position 180 - Master offset 90).
- This yields a slave command position of 144 (slave profile command 324 + slave offset (-180)).
- As the master axis moves positive, the slave position follows the profile.
- When the master axis position is at 270, the master position for profile calculation is 180 (270 - 90).
- This yields a slave command position of 0 (zero) (180 + (-180)).
- The slave follows the profile as the master axis moves until the master axis reaches a position of 450.
- The master axis position of 450 yields a master position for profile calculation of 360 (450 - 90).
- The slave command position is 0 (180 + (-180)).
- When the master reaches a position of 450, the slave commanded position remains at 0 (zero) since the Cyclic input is FALSE.
FBD Language Example
Not available.
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
(* MC_CamIn ST"Structured text" A high-level language that is block structured and syntactically resembles Pascal example *) //Inst_MC_CamIn is an instance of MC_CamIn
Inst_MC_CamIn( CamStartBool, Axis1, Axis2, 0.0, 0.0, 360.0, 360.0, 0, CamTableID, 0 );
See Also