![]()
 Function Block
Function Block![]() A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Disengages the slave axis from a MC_CamIn move.
A function block groups an algorithm and a set of private data. It has inputs and outputs. - Disengages the slave axis from a MC_CamIn move.
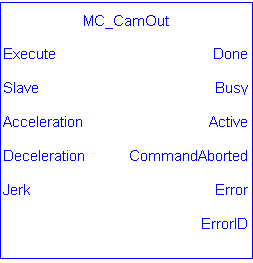
Inputs
|
Input |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Default |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Execute |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
No default |
On the rising edge |
|
Slave |
AXIS_REF |
1, 256 |
N/A |
No default |
Name of a declared instance of the AXIS_REF library function.
|
|
Acceleration |
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Acceleration rate. S-curve: Maximum acceleration. See S-curve and Trapezoidal Acceleration / Deceleration for more information. |
|
Deceleration |
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec2 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: Deceleration rate. S-curve: Unused. See S-curve and Trapezoidal Acceleration / Deceleration for more information. |
|
LREAL |
No range |
User unit/sec3 |
No default |
Trapezoidal: 0 (zero). S-curve: Constant jerk See S-curve and Trapezoidal Acceleration / Deceleration for more information. |
Outputs
|
Output |
Data Type |
Range |
Unit |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Done |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates the axis is disengaged from its master. |
|
Busy |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates this function block is executing. |
|
Active |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates this move is the Active move. |
|
CommandAborted |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates the move was aborted. |
|
Error |
BOOL |
0, 1 |
N/A |
Indicates either:
|
|
ErrorID |
INT |
No range |
N/A |
When the Error output is:
See PLCopen Function Block ErrorIDs for more information. |
Remarks
-
- This function block starts a motion-related action and stores data for calculations and error checking.
See Call Function Blocks Multiple Times in the Same Cycle if using a dual-core controller.
- See Function Blocks - General Rules for more information about how inputs and outputs work.
- If this function block is called and the active move is not a MC_CamIn move, this function block returns an error and the active move is not aborted.
- This function block:
- Aborts the active MC_CamIn move.
- Disengages the axis from its master.
- Disengages the slave axis from a MC_CamIn move.
- Commands the axis to continue at its current velocity.
- The axis continues to run at this velocity until this MC_CamOut move is aborted.
-
-
The current velocity is calculated by taking the average of the actual velocity during the previous 16 cycles.
Cancel the Cam Motion
- An alternative method to cancel the cam motion is a single axis move (MC_MoveAbsolute, MC_MoveRelative, MC_MoveAdditive, MC_MoveVelocity, and MC_Halt) with the BufferMode input set to 0 (zero).
- This cancels the MC_CamIn function and starts the new motion function on the slave axis.
- Many applications prefer calling MC_Halt instead of MC_CamOut because it does not send a velocity command to the slave axis.
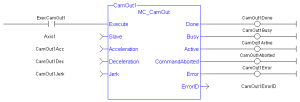
Figure 6-246: MC_CamOut
FBD Language Example
Not available.
FFLD Language Example
IL Language Example
Not available.
ST Language Example
(* MC_CamOut ST example *)
Inst_MC_CamOut(ExecCamOut1,Axis1,CamOut1Acc,CamOut1Dec,CamOut1Jerk);
//Inst_MC_CamOut is an instance of MC_CamOut
See Also